spooony
Club Captain
I created this malware guide some time ago on another hardware site. This is the shorter version of and maybe it can help someone out here one day. Please let me know for broken links so I can fix them. Also the images I used I got to thank Bleepingcomputer for it. My originals was deleted with my previous Photobucket account so I had to borrow theirs. Its uploaded to my new account so Admins don't worry I'm not leeching bandwidth. Anyways Enjoy 
For those that struggle to get pesky malware of your system here is a easy guide to follow to remove most malware.
REMEMBER IF ITS A FILE INFECTOR LIKE VIRUT OR SALITY THEN THIS WILL NOT WORK. YOUR ONLY WAY WILL BE WITH A BOOT DISK LIKE HIRENS BOOT CD AND SCAN YOUR SYSTEM OFFLINE.
Here is how to make a Usb boot disk with it
Or you can use the Dr. Web Live Cd
Remember Virut contains a bug in its code making any file it infects close to impossible to disinfect. A complete format and OS reinstall is advised with Virut.
Here are some info about this nasty polymorphic virus
Virut information
AVG Free | Win32/Virut.A
Follow these steps do not skip any!!
Make sure your in normal mode first. Go to start-> msconfig (remember to right click run as admin) then make sure normal startup is selected. If not. Select it and boot into normal mode. If you can't boot into normal mode. Then run in safe mode.
1. Enable Windows Firewall
Go to the cmd prompt and enter the following commands one by one
Ipconfig /flushdns /c
Netsh winsock reset
Netsh winsock reset catalog
Netsh interface reset all
Netsh firewall reset
Then reboot your computer
If you have Browser Redirection problems download GooredFix from one of the locations below and save it to your Desktop .
Download Mirror #1
Download Mirror #2
Ensure all Firefox windows are closed.
XP users run the tool, double-click it
Windows 7/Vista users right-click and select Run As Administrator .
When prompted to run the scan, click Yes .
GooredFix will check for infections, and then a log will appear.
If you have multiple Antivirus applications installed remove one. Same with firewall. Only have 1 AV solution and 1 firewall solution on your pc.
3. Cleaning
First go to Add/remove programs and look for entries like these
MyWay or MyWay Search Assistant
Viewpoint Manager (Remove Only)
Viewpoint Media Player
Viewpoint Toolbar
Viewpoint Toolbar (Remove Only)
Download latest version of Java Runtime Environment and save it to desktop. Do not save anything under my users documents or in a temp folder.
Do not install it. You have to remove older versions of Java first. You can do it with one of the following two methods:
FIRST METHOD
Download JavaRa to your desktop and unzip it to its own folder.
Run JavaRa.exe ( Vista users! Right click on JavaRa.exe , click Run As Administrator ), pick the language of your choice and click Select.
Then click Remove Older Versions .
Accept any prompts.
2ND METHOD
Go to Add remove programs and uninstall all your older java versions first. When everything is uninstalled install the latest version.
Same with Adobe flash. Use the Adobe Flash Uninstaller to uninstall it then install the latest version of Flash Player
Remove all the files from your antivirus quarantine and empty your recycle bin.
Download and Install CCleaner
Install it and run the cleaner once. When your done close it.
4. Disable disk Emulation tools
Disable any disk Emulation tools like Daemon tools, power Iso etc etc. Its very important do not skip this!
To do this download Defogger
Run it. Click on disable button and it ask to reboot click yes.
Download the following applications and save them to the desktop. Make sure your time and date is correct!
DO NOT RUN ANY OF THEM UNTIL INSTRUCTED!
Just note, when you download and run RKill, certain anti-virus programs may state that the program is a security risk. This is because some of the tools used by RKill can be used for good or bad, though the programs themselves are perfectly harmless, and most anti-virus programs just lump them into the bad category.
RKill.com Download Link
RKill.exe Download Link
RKill.scr Download Link
eXplorer.exe Download Link
iExplore.exe Download Link
WiNlOgOn.exe Download Link
uSeRiNiT.exe Download Link
Note: eXplorer.exe may trigger an alert from MBAM. It can be ignored and is safe.
The other filenames are RKill as well, just renamed in order to allow it run by certain malware.
SuperantiSpyware
Malware Bytes
Combofix (IMPORTANT RENAME IT TO JeniP.com when saving it TO desktop)
Tdskiller
MGtools
Disable your security software. If your using windows firewall leave it enabled. Third party firewalls its best to disable them as they can interfere with the cleaning.
If you got Spybot Search and Destroy make sure its Tea Timer is disabled. VERY IMPORTANT!!!!!
If you have AVG antivirus installed, download the AVG UNINSTALLER uninstall it.
For Vista users disable UAC
1.Click Start , and then click Control Panel .
2.In Control Panel , click User Accounts .
3. In the User Accounts window, click User Accounts .
4. In the User Accounts tasks window, click Turn User Account Control on or off .
5. If UAC is currently configured in Admin Approval Mode, the User Account Control message appears. Click Continue.
6.Clear the Use User Account Control (UAC) to help protect your computer check box, and then click OK . If it is already uncheck, then you should also notice a red shield with an X in it located in your system tray. Ignore any messages about UAC being disabled.
7.Click Restart Now to apply the change right away. (Restart even if you did not make the above change, we need to be sure that a reboot has occurred since the first time that UAC was disabled.)
Do NOT continue untill UAC has been disabled.
For Windows 7 users disabling UAC
1.Click Start , and then click Control Panel .
2.Click User Accounts and Family Safety
3.In the User Accounts and Family Safety window click Change User Account Control Settings
4.Then move the Slider all the way to the bottom to Never Notify
5. Click OK and then Yes to the popup warning that you are turning off UAC
6.If it is already unchecked, then you should also notice a red shield with an X in it located in your system tray. Ignore any mesages about UAC being disabled.
7.Click Restart Now to apply the change right away. (Restart even if you did not make the above change, we need to be sure that a reboot has occurred since the first time that UAC was disabled.)
6. Scanning
Install and Run the applications in the following order. If prompted to reboot do so.
Rkill
When RKill is run it will display a console screen. That console screen will continue to run until it RKill has finished. Once finished, the box will close and a log will be displayed showing all of the processes that were terminated by RKill and while RKill was running. Depending on the malware that is installed on the computer, when you run RKill you may see a message from the malware stating that the program could not be run because it is a virus or is infected.
These warnings are just fake alerts by the malware that has hijacked your computer trying to protect itself.
Two methods that you can try to get past this and allow RKill to run are:
When you receive the warning message, leave the message on the screen and try running RKill again.
If that does not work, just keep launching RKill until it catches and stays up long enough to kill the malware
Yes, both methods are not elegant, but they will work if you keep trying. Unfortunately, there is not much better I can do at this point for some malware that are very tenacious at killing all processes that run.
SuperantiSpyware
Double-click the icon on your desktop named SUPERAntiSpyware.exe. This will start the installation of SUPERAntiSpyware onto your computer.
When the installation begins, keep following the prompts in order to continue with the installation process. Do not make any changes to default settings, and when the program has finished installing, click on the Finish button to get back to your Windows desktop.
SUPERAntiSpyware will now automatically start and you will see a message asking you to select the language you would like the program to use. Please select your language and then press the OK button to continue.
You will now be prompted to update the SUPERAntiSpyware definitions. Please press the Yes button to allow the program to download and install the latest updates so that it can properly detect and remove the latest malware.
Please click on the Preferences button to customize how SUPERAntiSpyware will scan your computer.
When the program's preferences screen opens, click on the Scanning Control tab and put a checkmark in the following options
Close browsers before scanning.
Scan for tracking cookies.
When done, the settings on the Scanning Control preferences screen be similar to the image below.
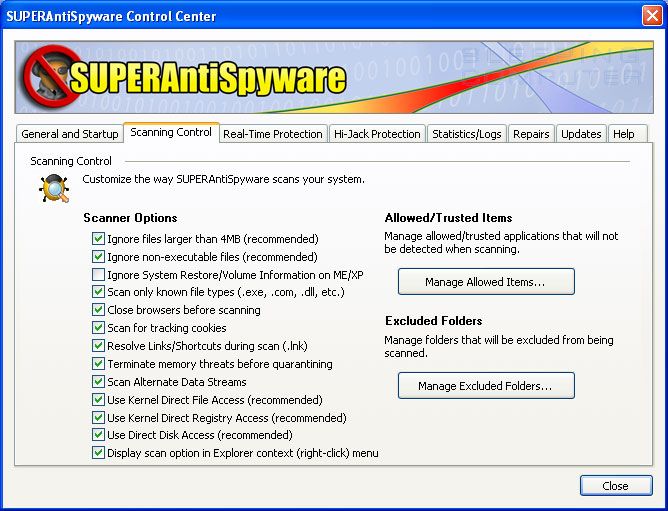

Now press the Close button to go back to the main screen.
You will now be at the main screen and should click on the Scan your Computer... button to begin the scanning process.
You will now be at the Scan page where you can choose the type of scan you would like to perform.
When the scan is finished a screen will appear showing the summary of what was detected.
You should click on the OK button to close the summary screen box and continue with the removal process.
MalwareBytes
Malwarebytes is designed to run best in Windows normal mode. If you can run it in normal mode, then you should. If you cannot run it in normal mode, run it in safemode; however, once you have the system running better, you should scan again in normal mode.
If installation fails, simply rename the downloaded file (mbam-setup.exe) to a random name, and try running it again.
When the installation begins, keep following the prompts in order to continue with the installation process. Do not make any changes to default settings and when the program has finished installing, make sure you leave both the Update Malwarebytes' Anti-Malware and Launch Malwarebytes' Anti-Malware checked. Then click on the Finish button.
MBAM will now automatically start and you will see a message stating that you should update the program before performing a scan. As MBAM will automatically update itself after the install, you can press the OK button to close that box and you will now be at the main program as shown below.
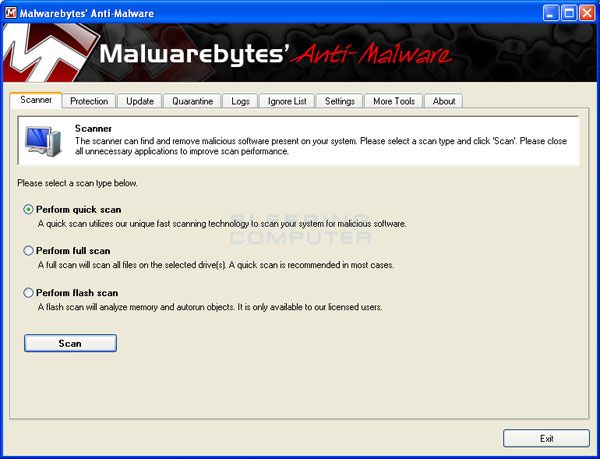

On the Scanner tab, make sure the the Perform full scan option is selected and then click on the Scan button to start scanning your computer for infections.
MBAM will now start scanning your computer for malware. This process can take quite a while, so I suggest you go and do something else and periodically check on the status of the scan.
When it's finished click on the Remove Selected button to remove all the listed malware. MBAM will now delete all of the files and registry keys and add them to the programs quarantine. When removing the files, MBAM may require a reboot in order to remove some of them. If it displays a message stating that it needs to reboot, please allow it to do so.
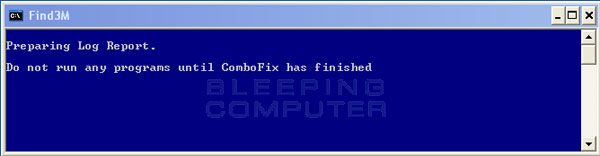
Combofix (Double Click on JeniP.com on your desktop)
ComboFix will now install itself on to your computer. When it is done, a blue screen will appear as shown below.

It will then back up the registry and ask if you want to installl the recovery console. Press yes

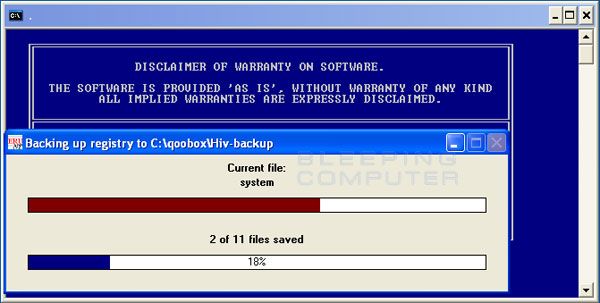
Once its done press yes again and you should see the following sequence
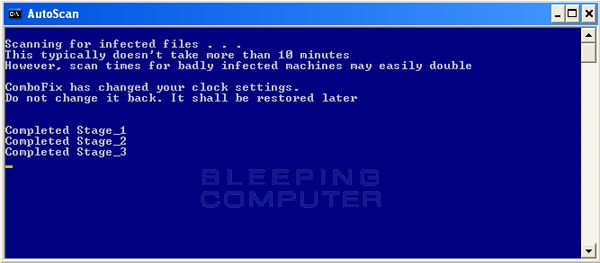

 When ComboFix has finished, it will automatically close the program and change your clock back to its original format.
When ComboFix has finished, it will automatically close the program and change your clock back to its original format.
Tdskiller
Extract and Execute TDSSkiller.exe
Press Start Scan
If malicious software was found then make sure cure is selected. If there is no option to 'Cure' its critical that you select skip.
Click continue ->Reboot now
MGtools
Just double click on the mgtools.exe and let it run
When your done you need to enable UAC again.
Navigate into the \\MGTools folder just created in the root of your Windows boot drive.
*.locate the EnableUAC.reg file and double click on it and allow it to be added to the registry.
*.This registry patch is used to enable the User Account Control feature
*.You should reboot after applying the registry patch so that it works properly.
When that is done disable system Restore and enable it again.
For Windows 7
1. Click Start
2. Right click Computer > Properties > Choose Advanced System Settings option in left menu listing.
3. Click System Protection tab
4. Then highlight the drive you wish to turn off System Restore and click Configure
5. Then choose Turn off system protection
6. Click Apply > OK
Reboot
To re-enable follow steps 1 - 4 and then choose Restore system settings and previous versions of files > Apply and OK
For Vista
1. Click Start
2. Right click Computer > Properties > Choose Advanced System Settings option in left menu listing.
3. If UAC enabled you will get a UAC prompt at this click Continue
4. Click System Protection tab
5. Then Untick any Drive Listed and in the popup window click Turn Off System Restore
6. Click Apply > OK
7. Reboot
To enable repeat the above steps
Run Ccleaner once.
Remember to save all the applications you download on another spot as OTL is going to remove them and clean up the pc.
To cleanup download OTLcleaner
Click on the Green Clean Up button
If your still having issues upload the mgtools.zip folder. It contains all the logs of the applications above.
To help with not getting infected again or better pc security follow these guide lines.
System Repair
To repair any damage done by malware use Virus Effect Remover.
It is a repair tool Assists end-users to remove the effects, of either a live virus or left over by a virus (or trojan,) in most Windows® Operating Systems W98SE/WinXP/Win2K-All/Vista & Win7.
Repairs and fixes OS items such as : Taskmanager, Regeditor, MSconfig, Folder Options.

WINDOWS UPDATES
Keeping Windows up-to-date is your best bet in keeping your computer safe and secure. The second Tuesday of every month is known as Patch Tuesday. This is the day that Microsoft releases monthly hotfixes and service packs for software installed on your computer. Be sure you have the latest service pack, hotfix rollup, and/or updates installed on your computer. These patches resolve known issues and other bugs that would put your computer at risk.
It is recommended to use Microsoft Update to get updates for both Windows and other Microsoft software such as Office.
Recommended settings for Automatic Updates are
*. Automatic (Recommended)
*. Every day at 5:00 PM
You should not install any drivers from Windows Update, always get them from the manufacturer.
For those on a highspeed connection and having multiple computers in their homes, here is a wonderful application called WSUS
WSUS Offline Update downloads updates for Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Microsoft Office 2003/2007. It then creates an ISO for a CD/DVD that you can use to update computers without an Internet connection. This is a great tool for technicians and can also be easy to use for most users too.
ANTIVIRUS
Avira AntiVir Personal Edition is very light on resources and the detection rate of malware is outstanding, better than almost every other antivirus according to tests. However, there are some minor reservations.
First, AntiVir does not include web or e-mail scanning capabilities; this is only available in the paid version. The lack of an e-mail scanner is not really a disadvantage , it just means that AntiVir won't warn you of infected emails before you open them. But should you open an infected email, AntiVir will still spring into action, so it doesn't mean that you're not protected from email-based infections. Although AntiVir had signature updating problems in the past, this issue seems to be fixed now.
Avast! Free Antivirus is also an excellent free antivirus that is very popular. The antivirus detection rates is on par with AntiVir and Microsoft Security Essentials. Avast has the most features, with full real-time capabilities, including web, e-mail, IM, P2P and network shields, boot-time scanning, and a behavioural blocker. Avast is also light on resources. The newly released version 6 brings even more features including an internet site ratings plugin, script malware protection and a limited (non-configurable) sandboxing feature.
Security Essentials 4.1.522 Vista got good detection rates, particularly for rootkits. Even more impressive is that Security Essentials has very few false positives, is light on resources and is good at removal of existing malware.
Microsoft Security Essentials is a great choice for average users because of the minimal user interaction required. It automatically updates and removes threats. No registration is needed, apart from a quick validating of Windows, and there are no nag screens or advertisements.
The main downsides are the slow scan speeds and the lengthy amount of time it takes to quarantine malware. MSE also is not available in certain countries so users there will have to look elsewhere. Note that Microsoft Security Essentials requires a genuine copy of Windows to install.
Panda Cloud Antivirus is Panda's successful attempt to jump on the free antivirus bandwagon. With a simple interface and completely automated features with automatic updating and removal of malware, it is an excellent choice for average users. The detection level is generally very high, but detection of zero day threats is slightly lower. PAC has a behavioural blocker and web protection, which will certainly increase your security, however I will only compare the AV component as you can simply use one of the other free AV's with a separate behavioural blocker
Comodo Internet Security is the free, multi-layered security application that keeps hackers out and personal information in.
Built from the ground upwards with your security in mind, Internet Security offers 360° protection by combining powerful Antivirus protection, an enterprise class packet filtering firewall, advanced host intrusion prevention and automatic sandboxing of unknown files.
Unlike the stripped down versions of commercial software that other software vendors offer for free, this is the full, completely functional version of the product.
Internet Security Includes:
Antivirus: Tracks down and destroy any existing malware hiding in a PC.
Anti-Spyware: Detects spyware threats and destroys each infection.
Anti-Rootkit: Scans, detects & removes rootkits on your computer.
Bot Protection: Prevents malicious software turning your PC into a zombie.
Defense+: Protects critical system files and blocks malware before it installs.
Auto Sandbox Technology™: Runs unknown files in an isolated environment where they can cause no damage.
Memory Firewall: Cutting-edge protection against sophisticated buffer overflow attacks.
Anti-Malware Kills malicious processes before they can do harm.
Second Opinion Scanners
Hitman Pro - If your child is not feeling well and you suspect he or she has a virus infection you're going to visit your doctor. But what do you do when the doctor tells you that he cannot find anything but your child still does not feel very well? Of course, you go to visit another doctor for a second opinion.
This is the same what Hitman Pro does for your computer. Hitman Pro is a second opinion scanner, designed to rescue your computer from malware (viruses, trojans, rootkits, etc.) that have infected your computer despite all the security measures you have taken (such as anti virus software, firewalls, etc.).
Hitman Pro is designed to work alongside existing security programs without any conflicts. It scans the computer quickly (less than 5 minutes) and does not slow down the computer (except for the few minutes it is scanning). Hitman Pro does not need to be installed. It can be run straight from a USB flash drive, a CD/DVD, local or network attached hard drive.
Computer users can use the Free Scan of Hitman Pro as a quick check (less than 5 minutes) to ensure that the existing anti virus program has not missed a threat.
Help Desk and Support organizations can use the Free Scan of Hitman Pro as a quick check for viruses and other malware. It can be run from USB or CD/DVD. No installation is required.
Website owners can offer the Free Scan of Hitman Pro as a service to visitors for a quick second opinion.
Hitman Pro offers you a Free Scan for a second opinion. It is designed to check if your security measures work. If nothing is found (and we sincerely hope so), then you will never need a license. When a virus is found, then you will receive a free 30-day license to remove the threat.
FIREWALLS
What is a network firewall?
What can a firewall protect against?
Some firewalls permit only email traffic through them, thereby protecting the network against any attacks other than attacks against the email service. Other firewalls provide less strict protections, and block services that are known to be problems.
Generally, firewalls are configured to protect against unauthenticated interactive logins from the "outside'' world. This, more than anything, helps prevent vandals from logging into machines on your network. More elaborate firewalls block traffic from the outside to the inside, but permit users on the inside to communicate freely with the outside. The firewall can protect you against any type of network-borne attack if you unplug it.
Firewalls are also important since they can provide a single "choke point'' where security and audit can be imposed. Unlike in a situation where a computer system is being attacked by someone dialing in with a modem, the firewall can act as an effective "phone tap'' and tracing tool. Firewalls provide an important logging and auditing function; often they provide summaries to the administrator about what kinds and amount of traffic passed through it, how many attempts there were to break into it, etc.
This is an important point: providing this "choke point'' can serve the same purpose on your network as a guarded gate can for your site's physical premises. That means anytime you have a change in "zones'' or levels of sensitivity, such a checkpoint is appropriate. A company rarely has only an outside gate and no receptionist or security staff to check badges on the way in. If there are layers of security on your site, it's reasonable to expect layers of security on your network.
Proactive firewalls have the most extended protection, including HIPS or program monitoring (HIPS Explained), and watch for malicious behavior before malware gets a chance to take control of your PC or turn it into a botnet drone. They seek to achieve stronger "2-way" protection, preventing programs from broadcasting your personal information to the Internet.
Some kinds of malware are best detected by their behavior, so a proactive firewall (or firewall/HIPS combo) is a solid second layer of protection next to your antivirus program. It's an excellent option for high risk users.
The built-in Windows firewall is a common choice since it passes all inbound tests (both stealth and open port) and doesn't have many popup alerts. It doesn't require installation, so it's not likely to conflict with your other programs. And many average users wouldn't reliably handle the popup alerts of the best firewalls on the market (especially at their max settings).
If you scan clean for malware and you don't want the features of a third-party firewall, then the Windows firewall is a practical and useful solution.
You can replace the Windows firewall with a basic third-party firewall for easier control of outbound protection and additional features. Most simple two-way firewalls ask you to allow or deny Internet access for unknown programs. Many automatically allow trustworthy apps and remember your decisions to become silent over time.
What can't a firewall protect against?
Firewalls can't protect against attacks that don't go through the firewall. Many corporations that connect to the Internet are very concerned about proprietary data leaking out of the company through that route. Unfortunately for those concerned, a magnetic tape can just as effectively be used to export data. Many organizations that are terrified (at a management level) of Internet connections have no coherent policy about how dial-in access via modems should be protected. It's silly to build a 6-foot thick steel door when you live in a wooden house, but there are a lot of organizations out there buying expensive firewalls and neglecting the numerous other back-doors into their network. For a firewall to work, it must be a part of a consistent overall organizational security architecture. Firewall policies must be realistic and reflect the level of security in the entire network. For example, a site with top secret or classified data doesn't need a firewall at all: they shouldn't be hooking up to the Internet in the first place, or the systems with the really secret data should be isolated from the rest of the corporate network.
Another thing a firewall can't really protect you against is traitors or idiots inside your network. While an industrial spy might export information through your firewall, he's just as likely to export it through a telephone, FAX machine, or floppy disk. Floppy disks are a far more likely means for information to leak from your organization than a firewall! Firewalls also cannot protect you against stupidity. Users who reveal sensitive information over the telephone are good targets for social engineering; an attacker may be able to break into your network by completely bypassing your firewall, if he can find a "helpful'' employee inside who can be fooled into giving access to a modem pool. Before deciding this isn't a problem in your organization, ask yourself how much trouble a contractor has getting logged into the network or how much difficulty a user who forgot his password has getting it reset. If the people on the help desk believe that every call is internal, you have a problem.
Lastly, firewalls can't protect against tunneling over most application protocols to trojaned or poorly written clients. There are no magic bullets and a firewall is not an excuse to not implement software controls on internal networks or ignore host security on servers. Tunneling "bad'' things over HTTP, SMTP, and other protocols is quite simple and trivially demonstrated. Security isn't "fire and forget''.
How can I test my firewall?
To test your firewall's ability to protect against incoming attacks and scans, visit one or more of the following sites. Note that if you are using a router, the test will target the router, not any software firewall your PC is running.
Shields UP!
PCFlank
Sygate Online Scan
HackerWhacker
Please note that while your firewall may report these scans as an "attack", you should not report this to any ISP. The Outpost Online Scans - What to do with Open and Closed Ports has more information about what the results mean and what action to take.
Outpost Security Suite Free Provides antivirus and firewall protection from both inbound and outbound attacks and is also much easier on the user when gaming or using fullscreen applications. If you already have one of the above anti-virus solutions Outpost will automatically detect this and disable/not install their anti-virus.
Online Armor Personal Firewall 's RunSafer is another option which I really like. It is very easy to use; you just select a program and click "Run Safer" and the program will now run with with restricted priviledges.
ZoneAlarm Free 10.2.078.000 is an excellent inbound/outbound OS firewall solution suited for users of every level of experience. ZoneAlarm protects systems from intrusions as well as program access to the web. ZoneAlarm features an easy-to-understand user interface. Users can adjust security settings for their needs to allow for file/printer sharing, public networks, and even turn off the firewall if ever needed. Simple controls in the form of visual slide bars make setting up this firewall a snap. ZoneAlarm offers to help users setup initial program access with a first-run scan of installed software and allows/denies accordingly. This first scan does not always offer accurate access to programs.
Users will have to interact with this firewall for a time after installation to make sure programs needing LAN or internet access are granted proper permissions. Pop ups are very simple in format offering Deny, Accept,and a checkbox a user can check to make ZoneAlarm remember the decision. Novice users should be able to easily identify the name of the program asking for web access so they can make the appropriate decision.
The Program Control will allow users to set ZoneAlarm for Low, which is a learning mode and no OS firewall protection and limited pop ups. Or users can choose Medium, which will make programs ask for permission to access the trusted and internet zones. The high setting is not offered in the Free version of ZoneAlarm. The Smart Defense Advisor will help reduce pop ups by offering settings for programs asking for access, based on the decisions made by other users worldwide. Users can choose whether or not to participate in ZoneAlarm's community defense program. Users can set programs access manually at anytime by going to ZoneAlarm's Program Control and selecting Programs.
Internet Zone controls are divided into the Trusted Zone, used for the local network to share files, printers, etc., and the Internet Zone for communication to/from the web. A simple 3-position format allows users to choose from "No protection" (firewall is off), Medium (Allows file/printer sharing), and High (will allow users to connect to a network but will not allow anyone else to connect to your system). The medium setting is recommended for home networks with more than one system, and for users whose modem requires this setting. The high setting is most recommended for single-system web access (only one computer at home and modem does not require a home network setting), and for public areas such as cafes, restaurants, and hotels (etc.) with wifi.
ZoneAlarm Free offers basic two-way defense, stealth mode, and anti-phishing protection. However, it lacks HIPS or program-to-program protection.
You can go HERE for a very good guide setting up a firewall.
Look 'n' Stop: a Lightweight and Effective Personal Firewall
Look 'n' Stop Firewall has been around for years; it's a solid protect that provides excellent protection and is extremely light on resources.
32-bit and 64-bit editions of Windows are supported by Look 'n' Stop (LnS): Windows 7, Vista, XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows 2000, ME and 98. The Visual C++ Runtime Library is also required but you do not need to hunt for this required file because the installer will download and install it, if it detected missing.
Key Features of Look’n’Stop
Application Filtering LnS will alert you on any application that will use internet connection
Internet Filtering most firewall offer this feature to block or allow inbound and outbound data packets
Rule-based firewall you can create or modify new firewall rules
Advanced logging a neat feature in LnS is to have a log (simple or full logs) for any application of your choice. This is useful if you would like to monitor few or all applications network connections.
Plug-ins an option to extend the capability of Look n Stop firewall by activating available plug-ins
Look 'n' Stop includes an anti-flood log protection
The setup file is a small one mega-bytes file. It is extremely fast to download and to install, whatever Internet connection speed.
Available in 18 languages, Look 'n' Stop Firewall 2.07 is the most recent version of Look 'n' Stop Firewall, a reference firewall used world-wide since 2000.
Passwords
With the constant media bombardment about viruses, worms, hacking and crackers you’d be forgiven for believing that you shouldn’t touch the Internet with a ten footpole for fear of someone stealing your identity and running off with your life savings. But behind the news headlines and hype there is little more threat of that in the online world than there is from the risks of everyday theft or fraud. It is simply a matter of taking some simple precautions to protect yourself as you would when walking down the street or locking the house.
In these days of high speed "always on" broadband Internet connections the security of your of computer, files and privacy should be a priority. Unfortunately, a lot of people are leaving their virtual front doors unlocked, and giving crackers the green light to do as they wish, simply because they do not understand the risks and take the appropriate precautions.
The responsibility for this common lack of security falls squarely on the shoulders of the humble Windows operating system. The consumer versions of Windows 95, 98 and Me are based on code written back in the days before networks and modems became common, and certainly before computer security became the issue it is now. In fact the original foundations of Windows are based on MS-DOS 1.0 released back in 1981, and although obviously major improvements have been added since that time, the legacy of an insecure operating system remains.
So how do I create a strong password and make my OS a bit more secure?
Use 10 or more characters
Choose a combination of:
numbers
upper case letters
lower case letters
special characters such as ! $ * % @ # & -
(in some cases restrictions may apply )
Avoid passwords that are easy to guess or to crack
Dictionary words (mackerel, dandelion, millionaire)
Foreign words (octobre, gesundheit, sayonara)
Simple transformations of words (tiny8, 7eleven, dude!)
Names, doubled names, first name and last initial (mabell, kittykitty, marissab)
Uppercase or lowercase words (MAGAZINE, licorice)
An alphabet sequence (lmnop) or a keyboard sequence (ghjkl

Words that have the vowels removed (sbtrctn, cntrlntllgnc)
Easy ways to create and remember strong passwords
Use lines from a childhood verse:
Jack be nimble, Jack be quick = JbeN#jbq1
Use an expression inspired by the name of a city:
I love Paris in the springtime = 1LpntST!
Chicago is my kind of town = C1mYK0t
Use lines from a favorite song:
You can't always get what you want = uC4n+agwUw!
Change passwords every 6 months at least.
Change "first-time" passwords that are issued to you immediately.
Don't reuse old passwords.
Don't use the same passwords for work accounts that you do for personal accounts.
Whenever practical use unique passwords for all accounts
Don't write passwords down and leave them in places not always under your control.
Replace your passwords every 30 to 120 days.
Disable logon after a specified number of failed attempts.
Use SSH or SSL for remote server authentication.
Don't use programs that send passwords in plain text such as Samba, FTP,
Telnet, Pathworks V 4.0.
Don't use shared usernames and passwords.
Change or disable the common user names such as Guest and Administrator.
Log on at the lowest level needed for the work to be done.
Disable or remove unused accounts.
Securing Your Browser
Securing your browser is a great asset in protecting your computer. By properly securing your browser, you can stop all kinds of malware from getting in.
My first recommendation for safe browsing is a free program called Sandboxie , for Windows 2000 and later. It creates a special contained "sandbox" environment on your PC. While browsing within the virtual sandbox provided by Sandboxie, you are totally isolated from the vital portions of your PC, namely your operating system environment on your hard drive and memory locations for your current OS session. So any files you download are isolated to the sandbox. Similarly, any programs that are executed only do so within the sandbox, and*have no access to your normal files, the Windows operating system or any other part of your PC.
Usage is remarkably simple. To start a sandboxed browsing session, you just click the "Sandboxed Web Browser" icon on your desktop (or the Sandboxie icon from the Quick Launch tray) and this will launch your default browser in the sandbox. You can then use it in the normal way to browse to sites or download files. By default, files that are saved in the Desktop, My Documents or Favorites will have a prompt to ask you whether you want to save the file permanently. I suggest you add your default downloads folder to the Quick Recovery settings so files saved there will be automatically saved to your real hard disk, saving you the trouble of manually recovering files.
After you have finished browsing, you can right click the Sandboxie icon and delete all sandboxed files and processes, and your PC will be returned to the same state it was in before the browsing session. You can change configuration settings to automatically delete all the sandboxed contents when you close a sandbox. You can also configure a third-party program, such as Eraser or SDelete, to erase the sandboxed contents for greater privacy.
The advantage is clear: any virus, trojan, worm, spyware or adware threats that"infected" your PC while browsing will be eliminated.
Sandboxie allows for in-depth configuration which increases security. For example, you can set it to block access to your personal files, or only allow certain programs to run or connect to the internet in a sandbox. A recent feature of Sandboxie also allows you to run sandboxed programs in a Limited User Account , similar to DropMyRights, for even greater security. This should also prevent most keyloggers from running.
However, there are some downsides to this approach. Firstly, if you want to update your browser addons/widgets, you'll need to open an un-sandboxed browser and do it from there. This also applies to bookmarks but you can configure Sandboxie to automatically retain those. Secondly, Sandboxie is not designed to detect or disable keyloggers . You can get around this (mostly) by always empty your sandbox before you log in to important sites (such as sites involving financial transactions). Thirdly, some people find the nag screen inconvenient, which appears for five seconds before a sandboxed application opens.
Sandboxie works fine with all browsers and most software applications, including e-mail clients (though this requires special configuration ), instant messaging clients, Bittorrent clients and games. However, it won't work with system software (software which installs a system driver).
GesWall is another excellent option. It automatically isolates certain applications (browsers, PDF viewers and file archivers) as well as files, registry keys, processes made by those applications. The generic rules for an isolated application are that the application:
1. Can read but cannot modify trusted resources.
2. Cannot read or modify confidential resources.
3. May create new untrusted resources, e.g. files.
4. May read or modify untrusted resources.
Known applications also have pre configured rules so those applications can run properly.
In effect, files which you download will not be able to access critical areas on your computer, similar to a Limited User Account. So any malware which you in adverdently download cannot execute and damage your computer. GesWall also allows for detailed customization where you can configure the restrictions of untrusted applications.
Overall, GesWall provides excellent security, and is a worthy alternative to Sandboxie.
KeyScrambler - Using advanced encryption algorithms, KeyScrambler encrypts your keystrokes deep in the kernel, as soon as they enter the computer.
When the encrypted keystrokes finally arrive at the intended application, the decryption component of KeyScrambler goes to work, and you see exactly the keys you've typed.
This way, as your keystrokes go through the different layers of the operating system, it doesn't matter if they get logged, or whether the keyloggers are known or brand new, because your keystrokes are completely indecipherable the whole time.
If you're up for it, consider making LastPass your easy, any-browser, any-OS solution , or get into KeePass for even tighter, more customized security.
Not up for installing something new and setting it all up? Then simply fix up your current browser's password-saving system.
Firefox can save your passwords, but does so insecurely, so that anyone who grabs your laptop, or digs into your files, can read them. So be sure to enable the Master Password , and while you're at it, install Master Password for a less-annoying, more-secure tool.
Chrome can save your passwords, too, and also sync them through the Google cloud to any other Chrome browser you use. But be sure to protect your passwords with a pass phrase .
Internet Explorer , even in its pre-release ninth version, doesn't offer much in the way of password protection, beyond a toggle to ask you before saving each password. You're best off getting friendly with LastPass .
Enable HTTPS and Better Security Everywhere You Can
If you're surfing without an encrypted connection, you're leaving yourself open to, at best, a practical joke from friends; at worst, a breach of security in your social networks, email, or other accounts, which can lead to further harm. It seems like paranoia, unless you've had a tech-savvy friend prove to you just how open you are.
Most sites that you'd want to use now offer an encrypted connection option, usually termed as "HTTPS" or "SSL". If a site doesn't have that option, and it's holding your personal data, consider whether you really need to be using that service. Here are the services for which you should definitely enable the secure/https option:
Gmail
Secure connections are usually a default now, but double-check: head into Settings, look under "Browser connection," and ensure that "Always use https" is enabled. (Be sure, too, that you've enabled two-step verification for your Google account , Gmail included.
Facebook
Recently offered , and not enabled by default. To make use of it, click the Account link on any Facebook page while logged in, head to Account Settings , then, under "Account Security", hit the change button and check the box that says"Browse Facebook on a secure connection (https) whenever possible." Hit the Save button and head elsewhere.
Yahoo
Yahoo has a lot of really great, personalized account security options so why aren't you using them? Logged into any Yahoo page, click under your name (in the "Hi NAME" link), and choose Account Info. You'll have to enter your password again (but, hey, that's good!), but then you can set custom password reset questions, require an SMS code for verification, set up an alternate email address for account recovery, and many more really good options that are both free and easy to use.
Hotmail
Now offered for everyone, though not fully supported across clients like Outlook and Windows Live Mail. If you're mostly using Hotmail in your browser, add an "s" to your Hotmail URL (https://hotmail.com), and you should see a screen asking you if you always want to use a secure connection. You probably do.
eBay/PayPal
Log into PayPal, click the My Account tab, then click the Profile sub-tab. Look for the "Security Key" tab. For $5, you can order a passphrase that arrives in physical form, and without which PayPal won't let anyone come close to your money. For those who do a decent amount of trading, especially overseas, it's a worthy investment.
Take a tip from Jeff Atwood, who found that, despite his best intentions, he had a fake anti-virus app installed on his machine. The culprit was a Java plug-in that allowed a site Atwood was passing by to sneak in some badly behaved code.
First things first: head to Mozilla's super-handy Plugin Check page , which works with almost any browser, and see which of your plug-ins need updating now. You'll probably be a bit surprised, as even I was.
Chrome has a few good options for keeping insecure plug-ins at bay. You can set them to "click-to-play" or disable them indivually , or enter about:flags into your address bar and enable the "Disable outdated plugins" option to automatically shut down plug-ins that have known vulnerabilities.
Firefox will work some automatic plug-in monitoring into its future versions, as will other browsers; for now, consider making Plugin Check something you visit frequently maybe even as one of your multiple startup pages.
SpywareBlaster 4.6 - This excellent product will protect both Internet Explorer and Firefox. Unfortunately it does not cover Opera.
SpywareBlaster adds a large list of malicious websites to Internet Explorer's Restricted Sites list. It also restricts malicious ActiveX components and ad/tracking cookies. The Firefox protection also blocks ad/tracking cookies.
EULAlyzer
One risk too many people take with software is not reading the End User License Agreement. This is understandable as many agreements are long and complicated. The problem is you may be exposing yourself or your machine to undesirable conditions. There aren't any shortcuts to the review process, but there is a free EULA analyzer software package that can flag interesting items for you in software license agreements or privacy policies.
If you're not familiar with the term EULA, it's an acronym for End User License Agreement. It's a contract you and the software provider enter which covers items ranging from copyrights to liabilities. Because of their complexity, many people accept the agreements without reading them. They want to believe there is nothing bad in the agreement, or in the software.
Some years back, it may have been safe to blindly accept the agreements. Today, more software packages or services infringe on your privacy or may use your PC and bandwidth. Others packages are categorized as ad-sponsored, which often contain clauses about serving advertisements or installing third party items. The result is we may be giving in or giving up in ways we didn't anticipate.
At first, I was a skeptical when I read about EULAlyzer program. After all, how well can a program interpret the terms we see in these software agreements? Then I noticed the same people who created SpyWare Blaster, which is a great tool, publishes EULAlyzer. It then occurred to me that Javacool Software was nicely suited for this task since they see many instances of how spyware and malware are embedded into software and the wording used in those software agreements.
As with their other programs, EULAlyzer is easy to use and provides a fast way to grab and copy a EULA or privacy policy. This involves dragging the programs + icon over the license agreement you'd like to review. The contents are then pasted into EULAlyzer. In some cases, such as web pages, you may have to do a copy and paste.
Spybot S&D Immunize - Adds a large list of malicious websites to Internet Explorer's Restricted Sites list just as SpywareBlaster does. This can be found by clicking the Immunize button on the left side of Spybot Search & Destroy 2.0 RC2.
Web of Trust (WOT) - A free Internet security addon for your browser. It will keep you safe from online scams, identity theft, spyware, spam, viruses and unreliable shopping sites. WOT warns you before you interact with a risky website. This addon makes use of the OpenDNS project titled Phishtank to help detect bad websites. WOT is available as an add-on for Internet Explorer, and Mozilla Firefox and as a bookmarklet for Opera, Google Chrome, Safari, and any other browser supporting Javascript and bookmarks/favorites. After downloading the addon to the user's browser, the WOT logo appears in the web browser's navigation toolbar. When the user navigates to a website, the color of the logo will change color based on a traffic light system (Green, Light Green, Yellow, Light Red or Red); depending on the reputation of a website determined by its users.
SAFER INTERNET
You can add a layer of protection to your home network or computer by using OpenDNS
Many routers support adding OpenDNS in an easy to configure manner as well as several open-source firmwares. One such firmware is the Tomato firmware which is most commonly used on the WRT54GL router.
OpenDNS can help to filter out bad websites that contain adware and phishing attempts. It makes use of PhishTank which is a community based anti-phishing service. PhishTank is used by Opera, WOT, Yahoo Mail and by PhishTank Site Checker.
Its easy to setup. Go HERE for a guide to set it up
An account with OpenDNS is not required, it is recommended. Best of all it's free. Having an account allows you to filter out all types of websites.
Norton DNS uses Symantecs exhaustive Safe Web database. This is the database that underpins most of Symantecs security efforts, and brings together the results of its anti-malware research, anti-spam efforts and many more. Non-commercial efforts like malwaredomains.com, while highly useful and accurate, simply won¡¯t be able to compete with the volume of information Safe Web offers.
Currently it is free for non-commercial use, and takes nothing more than pointing your DNS client at the servers.
Currently 198.153.192.1 and 198.153.194.1
If you prefer not to muck about with network settings, Symantec has provided client software for both Windows and OSX. The client software acts as a local DNS repeater allowing you to bypass restrictions that may exist in using off-network DNS providers.
Comodo Secure DNS is a domain name resolution service that resolves your DNS requests through our worldwide network of redundant DNS servers. This can provide a much faster and more reliable Internet browsing experience than using the DNS servers provided by your ISP and does not require any hardware or software installation.
As a leading provider of computer security solutions, Comodo is keenly aware of the dangers that plague the Internet today. SecureDNS helps users keep safe online with its malware domain filtering feature. SecureDNS references a real-time block list (RBL) of harmful websites (i.e. phishing sites, malware sites, spyware sites, excessive advertising sites, etc.) and will warn you whenever you attempt to access a site containing potentially threatening content. Additionally, our 'name cache invalidation' solution signals the Comodo Secure DNS recursive servers whenever a DNS record is updated - fundamentally eliminating the concept of a TTL. Directing your requests through highly secure servers can also reduce your exposure to the DNS Cache Poisoning attacks that may affect everybody else using your ISP.
It's quick and easy to change to Comodo Secure DNS. No downloads and it's absolutely free.
156.154.70.22
156.154.71.22
No OS is safe. Not even Industrial systems.
Here is Nortons Dossier on Stuxnet
Malware Lingo
Adware
Adware is any type of advertising-supported software that will play, display, or download advertisements automatically on a user's computer once the software hasbeen installed on it or while the application is in use. Some adware can alsobe spyware due to its privacy-invasive characteristics.
BackDoor
A backdoor in a computer system (or cryptosystem or algorithm) is a means of circumventing regular authentication, securing remote computer access, accessing plain text, etc., while remaining to be undetected. A backdoor may appear to be an installed program or a modification to a program or hardware device that's already installed.
Baiting
Baiting uses tangible media and relies on the curiosity or greed of the victim. Baiting involves an attacker leaving a malware infected media such as a CD ROM or USB flash drive in a public place where it is likely to be found, appearing to be legitimate and appealing, and waits to be used by the victim. Baiting is easy to perform as in this example where an attacker might create a malware loaded CD with a company logo on it, and the words"Company Reorganization Plan" on the front. The media is left on the lobby floor ofthe targeted company. An employee could find it and then insert it into a computer to satisfy their curiosity. By inserting the CD into a computer to view its contents, the user unknowingly installs malware on it, allowing the attacker access to his computer and possibly, the company's computer network. If there is no mechanism to block the malware, then computers set to "auto-run" inserted media could be immediately compromised when the CD is inserted.
Botnet
Botnet is a collection of software robots, or bots, that are automatic and self-directed. Botnet is often associated with malware but can refer to the network of computers using distributed computing software.
Botnet generally refers to a group of compromised computers called zombie computers running software that is usually installed via worms, trojans or backdoors, under a common command-and-control infrastructure.
Browser plugin
A browser plugin is a software program that extends the capabilities of your Internet browser in a specific way. Not all browser plugins are harmful and some maybe helpful. This category contains mostly dubious browser plugins such as "Search Assistant", toolbars, etc. that have been known to transmit user data to their creators or have been installed using covert means.
Commercial Network
A commercial network management tool is mostly used in (large) corporations. It can log the network traffic passively (sniffing) or examine the logs of proxies, etc. Nothing is installed on the individual computers, the software runs on a central server. They can only log items that pass through the network, but not local items such as the entered passwords, keystrokes or screenshots.
Crimeware
Crimeware is a distinct type of malware designed to automate financial crime by performing identity theft to access online accounts of users at financial institutions and online retailers for the express purposeof stealing funds from those accounts or performing unauthorized transactions to the benefit of the thief controlling the crimeware. Crimeware is often used to export private information from a network for financial exploitation. Crimeware is viewed as a growing concern in network security as this type of threat seeks to steal confidential information.
Computer virus
A computer virus is computer software that has the ability to replicate itself and infect a computer without the informed consent or knowledge of the computer user. Certain malware, adware and spyware have been incorrectly termed as a virus because they lack the ability to copy themselves. A real virus spreads from one system to another through an executable code when its host is transferred to a target computer; such as being sent over a network or the Internet, email or transported via removable media such as a CD, DVD or USB drive. Infected files residing in a network file system or any instance where a computer can be accessed by another one increases the chances of spreading a virus infection.
The term "computer virus" is considered to be malware, a much broader term which also encompasses several types of malicious software including worms, trojans, and others. Although technically different, viruses are often confused with computer worms and trojans. Unlike a virus, a worm can take advantage of security holes in order to spread itself among other systems, while a trojan appears to be harmless but has an underlying plan. A worm, trojan or virus, once executed, can endanger a computers data, operation, or network ability. User awareness of some computer viruses and other malware may be readily apparent while many other types go unnoticed.
The increasing number of computers being connected to local area networks and the Internet is creating an environment for computer viruses to spread. Increased use of email and instant messaging are additional ways computer viruses spread.
Computer worm
A computer worm is a self-replicating computer program that sends copies of itself within a computer network and it can do so without any involvement by the user. A worm doesn't need to attach itself to an existing program in order to spread. Worms typically cause some harm to the network, most notably by consuming bandwidth.
Data miner
A data miner's primary function is to gather data about an end user. Some adware applications may employ data mining abilities.
Email bomb
An email bomb is a form of network abuse by sending enormous amounts of emails toan address in an attempt to overflow the mailbox or overwhelm the mail server where the email address is hosted in what is called a denial-of-service attack.
Email spoofing
Email spoofing is a fraudulent email activity in which parts of the email header and the sender address are modified, appearing as if the email was sent from another source. This technique is commonly used for spamming and phishing to conceal the origin of an email message. By altering certain properties of the email header, such as the From, Return-Path and Reply-To fields, fraudulent users can make the email appear to have been sent from someone other than the real sender.
Sometimes the source of the spam email is indicated in the Reply-To field. If the initial email is replied to, it will be delivered to the address specified in the Reply-To field, which might be the spammer's address. But most spam emails, especially malevolent ones carrying a trojan or virus, or those advertising a website, falsify this email address, sending the reply to another potential victim.
Exploit
An exploit is a portion of software, data, or string of commands that take advantage ofa computer bug, glitch or vulnerability disrupting normal behavior on computer software, hardware or other electronic device. Usually this includes seizing controlof a user's computer system or attacks that allow privilege escalation or a denial of service.
Fast flux
Fast flux, DNS technique, is used by botnets to conceal phishing and malware distribution sites behind a continuously changing network of compromised host systems utilized as proxies. Fast flux can also refer to a combined peer-to-peer network, distributed command and control, web-based load balancing and proxy redirection to make malware networks less detectable and more resistant to counter-measures.
Fast flux may be seen by Internet users in phishing attacks linked to crime organizations, including attacks on social networks.
Fraudulent dialers
Dialers are used to connect computers to the Internet but fraudulent dialers are designed to connect to premium-rate numbers. Fraudulent dialers are often installed through security holes in a computer's operating system and will change the computer settings to dial up through the premium-rate number. The additional monies are collected by the provider of the fraudulent number. Some dialers inform the user of benefits for usingthe special number to access special content which is usually illegal materials or downloads.
Users that have DSLs or other broadband connections are usually not affected since adial is dependent on regular phone lines. But, if an ISDN adapter or additional analogmodem is installed, the dialer may be able to connect.
Malicious dialers can be identified by:
A download popup opens when a website is opening.
The website may or may not discreetly display a price.
The download initiates even if the cancel button has been clicked.
Without any notice, the dialer installs as a default connection.
The dialer perpetuates unwanted connections without any user action.
No notice about the price is presented before dialing in.
While connected, the high price of the connection is not shown.
The dialer cannot be easily uninstalled if at all.
Hijacker
Hijacker is an application that attempts to take control of the user's homepage and replace it with one that the hijacker chooses. It is a low security threat, but is annoying. Most hijackers use stealth techniques or trick dialog boxes to perform installation.
Browser hijackers commonly do one or more of the following:
Change your "search" page and passes all searches to a pay-per-search site
Change your default home page to the company page. Sometimes the software changes them to a portal featuring porn sites.
May transmit URLs viewed toward the company server
Hoax
A hoax is an attempt to purposefully dupe an audience into believing something is real, when it actually is not what it appears or claims to be. A hoax can be made by using only true statements but with different context or wording. A hoax is often carried out as a practical joke, to cause embarrassment, or to create awareness to prompt social change. Many hoaxes are motivated to poke fun at, educate or point out the absurdity of the target.
Keylogger
A keylogger is surveillance software capable of recording all the keystrokes a user makes and saving that to a log file, which is usually encrypted. A keylogger recorder captures information entered on a keyboard including instant messages, email and any other type of information. Some keyloggers record email addresses the user uses and URLs that are visited. Thelog file created by the keylogger can then be sent to a designated receiver.
As a surveillance tool, keyloggers, are oftenused in the workplace by employers ensuring work computers used by employees are for business purposes only. However, keyloggers can be embedded in spyware allowing the user's information tobe sent to an unauthorized third party.
Loyaltyware
Loyaltyware is a sub-form of adware. Loyaltyware is a type of software that works around the concept of user loyalty by providing incentives in the form of cash,points, airline miles, or other type of goodswhile shopping.Loyaltyware
Malware
Malware, a term meaning "malicious software", refers to a set of computer instructions created for the express purpose of infiltrating a computer system, and modify, record, damage or transmit data without the permission of its owner. The term "malware" is generally used to describe any form of intrusive, hostile, or bothersome software application or code.
Malware covers a broad range of types, from cookies without consent used for tracking user surfing behavior, to more malevolent types such as viruses, worms, trojans, specific rootkits, spyware, adware,scareware, crimeware and other forms of malicious software. Certain government statutes define malware as a computer contaminant and is written into legal code in many states.
Parasiteware
Parasiteware is the term for any adware that by default overwrites certain affiliate tracking links. These tracking links are used by webmasters to sell products and tohelp fund websites. The controversy is centered on companies like WhenU, eBates,and Top Moxie, popular makers of adware applications. These companies release their software to assist users in getting credit for rebates, cash back shopping, or contributions to funds. To the end user, parasiteware represents little in the way of a security threat.
Phishing
Phishing is a criminally fraudulent process of collecting sensitive information such as usernames, passwords and credit card details by pretending to be a trustworthy entity in an electronic communication. Communications supposedly from well known social networks, auction sites, online payment processors or IT administrators are common fronts to bait the unsuspecting computer user. Phishing is commonly performed by email or instant messaging, directing users to enter details at a fake website that mimicks a legitimate one. Even when using server authentication, it may not be apparent that it is a fake website. An example of social engineering techniques, phishing is used to trick users, exploiting the weaknesses of web security technologies. The rising number of phishing scams has prompted and increase of legislation, training for the user, public awareness, and technical security procedures.
Pretexting
Pretexting is the practice of presenting on self as someone else for the purpose of acquiring sensitive information and is usually performed over the telephone. Presenting an invented scenario involves some prior research or using bits of known information such as data of birth or billing address to establish credibility with the targeted victim.
This method is often used in business to disclose customer information. Private investigators use this technique to acquire telephone, utility and bank records, and other information. This gives the investigator factual basis to establish legitimacy with managers of the business for even tougher questioning.
Many U.S. companies continue to use client verification by asking questions whose answers are supposedly known only by the client such as a Social Security Number or mother's maiden name, thus perpetuating this security problem even more.
Pretexting is also used to impersonate any individual who could be perceived by the targeted victim as have authority or right to know. The pretexter prepares answers that could potentially be asked by the targeted victim and must sound convincing to achieve his goal.
Rogue security software
Rogue security software uses malware or malevolent tools to advertise or install itself or forces computer users to pay to remove non existent malware. A trojan is often installed by rogue software when downloading a trial version, or it will run other unwanted actions. Rogue software makers want users to install and purchase their product. A common tactic to install their program, is to display fake Windows dialog boxes or other browser pop-up with messages that entice the user to click on them. Usually a message is displayed such as "WARNING! Your computer is infected with Spyware/Adware/Viruses! Buy [software name] to remove it!", another message is "Click OK to scan your system" without asking to buy the software. Yet another example is "Computer/Internet Connection/OS is not optimized and to Click Here to scan now".
Once the user clicks the OK button in the dialog box, he will be directed to a malicious website, which installs the program. Sometimes, clicking close window or X button in an attempt to close the dialog box will have the same effect. (To circumvent that trick, Press Alt F4 or use Ctrl-Alt-Delete to access the Task Manager). Some rogue software will download the trial version automatically without any user interaction. In addition to rogue programs being installed, many sites now use a technique to install multiple trojans at once by downloading a dropper first, loading various malware to the unsuspecting user's computer.
Rootkit
A rootkit is a software system containing one or more programs designed to show no indication that a system has been compromised. a rootkit is used to replace essential system executables, which can then conceal processes and files installed by the attacker as well as rootkit itself. A rootkit's intention is to control the operating system. Rootkits obscure their presence on the system through by evading standard operating system security mechanisms.
Rootkits can also be trojans, tricking the user into thinking they can be safely run on their systems. This can be achieved by concealing running processes from monitoring programs, or hiding files or system data from the operating system. Rootkits are also capable of installing a "back door" in a system by changing the login mechanism (such as /bin/login) with an executable that accepts a secret login combination, allowing the system to be accessed by an attacker, even if changes are made to the actual accounts on the system.
Originally, rootkits may have been normal applications, designed to take control of a faulty or unresponsive system, but more recently have been produced as malware allowing attackers to gain access to systems undetected. Rootkits exist for a variety of operating systems, such as Microsoft Windows, Linux, Mac OS, and Solaris. Rootkits often install themselves as drivers or kernel modules or modify parts of the operating system, depending on the internal elements of an operating system's mechanisms.
SMiShing
Smishing is a criminal activity that utilizes social engineering techniques similar to that of phishing. The name originated from"SMs phISHING". SMS or Short Message Service, is the technology behind text messaging on cell phones. Like phishing, smishing uses text messages on cell phones to lure a user into revealing personal information. The method used to actually "capture" user's information, or"hook", in the text message could be a website URL, although it is more typical that a phone number is displayed that connects to an automated voice response system.
Smurf attack
The Smurf attack is a means of producing a large amount of traffic on a computer network. This is a type of denial-of-service attack that overwhelms a target system via spoofed broadcast ping messages. In this case, an attacker sends a large volume of ICMP echo requests, or pings, to IP broadcast addresses, all having a spoofed source IP address of the targeted victim. If the routing device that delivers traffic to those broadcast addresses sends the IP broadcast to all the hosts, then many of the hosts on that IP network will take the ICMP echo request and send an echo reply, thus multiplying the traffic by the number of hosts that respond. Hundreds of machines on a multi-access broadcast network could reply to each packet.
Spamware
Spamware is software designed by or for use by spammers. Spamware can include the capability to import thousands of email addresses, generate random email addresses, insert fraudulent headers into messages, use multiple mail servers at once, and use open relays. Spamware can also be used to locate email addresses to build lists for spamming or to sell to spammers.
Spyware
Spyware is computer software that is installed on a user's computer without the user's express consent with the purpose of collecting information about the user, their computer or browsing habits.
As the term implies, spyware is software capable of secretly monitoring the user's behavior, but can also collect various types of personal information, including web surfing habits and websites visited.
Spyware can also impede the user's control of his computer by installing additional software, and redirecting web browser activity. Spyware is known to cause other interference by changing computer settings that slow connection speeds, load different home pages, and lose Internet connectivity or program functionality.
With the proliferation of spyware, an antispyware industry has sprung up. Use of antispyware software is now a widely accepted practice for the security of Microsoft Windows and desktop computers. A number of anti-spyware laws have been passed, targeting any software that is surreptitiously installed with the intent to control a user's computer. Due to its privacy-invasive characteristics, the US Federal Trade Commission has placed a page on their website advising consumers on how to lower the risk of being infected by spyware.
Trojan horse
The Trojan horse, or trojan, is a type of malware that appears to have a normal function but actually conceals malicious functions that it performs without authorized access to the host system. A Trojan can allow the ability to save their files on the user's computer or monitor theuser's screen and control his computer.
A trojan is not technically a virus but can be easily and unknowingly downloaded by the computer user. One example might be a computer game, when executed by the computer user, allows a hacker to control the user's computer. In this case the computer game is a trojan.
Vishing
Vishing is the unlawful practice of utilizing social engineering over the telephone system, using features of Voice over IP (VoIP) to access confidential personal and financial information from the public for financial reward. The term "vishing" is a combined form of "voice" and "phishing".
Vishing takes advantage of the public's trust in using landline telephone systems that end in physical locations recognized by the telephone company, and associated with a paying customer. VoIP makes previously anti-abuse tools or features of caller ID spoofing, complex automated systems (IVR), low cost, and anonymity for the paying customer widely available. Typically, vishing is used to capture credit card numbers or other sensitive information to be used in identity theft schemes by perpetrators.
Legal authorities find it difficult to monitor or trace vishing scams, although technology is used to monitor all PSTN based traffic, identifying vishing attempts as a result of patterns andanomalies in call activities. Consumers are advised to be suspicious when they receive messages prompting them to call and give their credit card or bank numbers. Usually, the consumer is directed to contact their bank or credit card company to verify the message.
VoIP spam
VoIP spam, is the proliferation of unwanted phone calls that are automatically-dialed with pre-recorded messages using Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP). Some even call it SPIT which stands for "Spam over Internet Telephony". Email, Internet applications and other Voice over IP systems are vulnerable to abuse by attackers who instigate unsolicited and unwanted communications.
Telemarketers, prank callers, and other telephone system abusers are increasingly targeting VoIP. The technology behind this threat is SIP (Session Initiation Protocol, IETF ¨C Internet Engineering Task Force, RFC 3261) which has has been supported by major telecommunication vendors, and could become the industry standard for voice, video and other types of interactive communication including instant messaging and gaming.
References
Useful Links & Recommended Threads - Wilders Security Forums
www.techsupportalert.com/
www.freedrweb.com/cureit/?lng=en
www.malwarebytes.org/mbam.php
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/.../bb897445.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/.../bb896653.aspx
www.glaryutilities.com/
http://miekiemoes.blogspot.com/2008/...gain-sigh.html
Emsisoft Knolwedgebase: What is a computer worm? Find and remove worms with Emsisoft Anti-Malware.
http://www.virusbtn.com/conference/v...astMinute7.xml
PC Security - Lunarsoft Wiki
http://forum.avast.com/index.php?topic=55588.0
http://www.spywareterminator.com/sup...s-spyware.aspx
RKill - What it does and What it Doesn't - A brief introduction to the program <-Thanks for Rkill

For those that struggle to get pesky malware of your system here is a easy guide to follow to remove most malware.
REMEMBER IF ITS A FILE INFECTOR LIKE VIRUT OR SALITY THEN THIS WILL NOT WORK. YOUR ONLY WAY WILL BE WITH A BOOT DISK LIKE HIRENS BOOT CD AND SCAN YOUR SYSTEM OFFLINE.
Here is how to make a Usb boot disk with it
Or you can use the Dr. Web Live Cd
Remember Virut contains a bug in its code making any file it infects close to impossible to disinfect. A complete format and OS reinstall is advised with Virut.
Here are some info about this nasty polymorphic virus
Virut information
AVG Free | Win32/Virut.A
Follow these steps do not skip any!!
Make sure your in normal mode first. Go to start-> msconfig (remember to right click run as admin) then make sure normal startup is selected. If not. Select it and boot into normal mode. If you can't boot into normal mode. Then run in safe mode.
1. Enable Windows Firewall
Go to the cmd prompt and enter the following commands one by one
Ipconfig /flushdns /c
Netsh winsock reset
Netsh winsock reset catalog
Netsh interface reset all
Netsh firewall reset
Then reboot your computer
If you have Browser Redirection problems download GooredFix from one of the locations below and save it to your Desktop .
Download Mirror #1
Download Mirror #2
Ensure all Firefox windows are closed.
XP users run the tool, double-click it
Windows 7/Vista users right-click and select Run As Administrator .
When prompted to run the scan, click Yes .
GooredFix will check for infections, and then a log will appear.
If you have multiple Antivirus applications installed remove one. Same with firewall. Only have 1 AV solution and 1 firewall solution on your pc.
3. Cleaning
First go to Add/remove programs and look for entries like these
MyWay or MyWay Search Assistant
Viewpoint Manager (Remove Only)
Viewpoint Media Player
Viewpoint Toolbar
Viewpoint Toolbar (Remove Only)
Download latest version of Java Runtime Environment and save it to desktop. Do not save anything under my users documents or in a temp folder.
Do not install it. You have to remove older versions of Java first. You can do it with one of the following two methods:
FIRST METHOD
Download JavaRa to your desktop and unzip it to its own folder.
Run JavaRa.exe ( Vista users! Right click on JavaRa.exe , click Run As Administrator ), pick the language of your choice and click Select.
Then click Remove Older Versions .
Accept any prompts.
2ND METHOD
Go to Add remove programs and uninstall all your older java versions first. When everything is uninstalled install the latest version.
Same with Adobe flash. Use the Adobe Flash Uninstaller to uninstall it then install the latest version of Flash Player
Remove all the files from your antivirus quarantine and empty your recycle bin.
Download and Install CCleaner
Install it and run the cleaner once. When your done close it.
4. Disable disk Emulation tools
Disable any disk Emulation tools like Daemon tools, power Iso etc etc. Its very important do not skip this!
To do this download Defogger
Run it. Click on disable button and it ask to reboot click yes.
Download the following applications and save them to the desktop. Make sure your time and date is correct!
DO NOT RUN ANY OF THEM UNTIL INSTRUCTED!
Just note, when you download and run RKill, certain anti-virus programs may state that the program is a security risk. This is because some of the tools used by RKill can be used for good or bad, though the programs themselves are perfectly harmless, and most anti-virus programs just lump them into the bad category.
RKill.com Download Link
RKill.exe Download Link
RKill.scr Download Link
eXplorer.exe Download Link
iExplore.exe Download Link
WiNlOgOn.exe Download Link
uSeRiNiT.exe Download Link
Note: eXplorer.exe may trigger an alert from MBAM. It can be ignored and is safe.
The other filenames are RKill as well, just renamed in order to allow it run by certain malware.
SuperantiSpyware
Malware Bytes
Combofix (IMPORTANT RENAME IT TO JeniP.com when saving it TO desktop)
Tdskiller
MGtools
Disable your security software. If your using windows firewall leave it enabled. Third party firewalls its best to disable them as they can interfere with the cleaning.
If you got Spybot Search and Destroy make sure its Tea Timer is disabled. VERY IMPORTANT!!!!!
If you have AVG antivirus installed, download the AVG UNINSTALLER uninstall it.
For Vista users disable UAC
1.Click Start , and then click Control Panel .
2.In Control Panel , click User Accounts .
3. In the User Accounts window, click User Accounts .
4. In the User Accounts tasks window, click Turn User Account Control on or off .
5. If UAC is currently configured in Admin Approval Mode, the User Account Control message appears. Click Continue.
6.Clear the Use User Account Control (UAC) to help protect your computer check box, and then click OK . If it is already uncheck, then you should also notice a red shield with an X in it located in your system tray. Ignore any messages about UAC being disabled.
7.Click Restart Now to apply the change right away. (Restart even if you did not make the above change, we need to be sure that a reboot has occurred since the first time that UAC was disabled.)
Do NOT continue untill UAC has been disabled.
For Windows 7 users disabling UAC
1.Click Start , and then click Control Panel .
2.Click User Accounts and Family Safety
3.In the User Accounts and Family Safety window click Change User Account Control Settings
4.Then move the Slider all the way to the bottom to Never Notify
5. Click OK and then Yes to the popup warning that you are turning off UAC
6.If it is already unchecked, then you should also notice a red shield with an X in it located in your system tray. Ignore any mesages about UAC being disabled.
7.Click Restart Now to apply the change right away. (Restart even if you did not make the above change, we need to be sure that a reboot has occurred since the first time that UAC was disabled.)
6. Scanning
Install and Run the applications in the following order. If prompted to reboot do so.
Rkill
When RKill is run it will display a console screen. That console screen will continue to run until it RKill has finished. Once finished, the box will close and a log will be displayed showing all of the processes that were terminated by RKill and while RKill was running. Depending on the malware that is installed on the computer, when you run RKill you may see a message from the malware stating that the program could not be run because it is a virus or is infected.
These warnings are just fake alerts by the malware that has hijacked your computer trying to protect itself.
Two methods that you can try to get past this and allow RKill to run are:
When you receive the warning message, leave the message on the screen and try running RKill again.
If that does not work, just keep launching RKill until it catches and stays up long enough to kill the malware
Yes, both methods are not elegant, but they will work if you keep trying. Unfortunately, there is not much better I can do at this point for some malware that are very tenacious at killing all processes that run.
SuperantiSpyware
Double-click the icon on your desktop named SUPERAntiSpyware.exe. This will start the installation of SUPERAntiSpyware onto your computer.
When the installation begins, keep following the prompts in order to continue with the installation process. Do not make any changes to default settings, and when the program has finished installing, click on the Finish button to get back to your Windows desktop.
SUPERAntiSpyware will now automatically start and you will see a message asking you to select the language you would like the program to use. Please select your language and then press the OK button to continue.
You will now be prompted to update the SUPERAntiSpyware definitions. Please press the Yes button to allow the program to download and install the latest updates so that it can properly detect and remove the latest malware.
Please click on the Preferences button to customize how SUPERAntiSpyware will scan your computer.
When the program's preferences screen opens, click on the Scanning Control tab and put a checkmark in the following options
Close browsers before scanning.
Scan for tracking cookies.
When done, the settings on the Scanning Control preferences screen be similar to the image below.


Now press the Close button to go back to the main screen.
You will now be at the main screen and should click on the Scan your Computer... button to begin the scanning process.
You will now be at the Scan page where you can choose the type of scan you would like to perform.
When the scan is finished a screen will appear showing the summary of what was detected.
You should click on the OK button to close the summary screen box and continue with the removal process.
MalwareBytes
Malwarebytes is designed to run best in Windows normal mode. If you can run it in normal mode, then you should. If you cannot run it in normal mode, run it in safemode; however, once you have the system running better, you should scan again in normal mode.
If installation fails, simply rename the downloaded file (mbam-setup.exe) to a random name, and try running it again.
When the installation begins, keep following the prompts in order to continue with the installation process. Do not make any changes to default settings and when the program has finished installing, make sure you leave both the Update Malwarebytes' Anti-Malware and Launch Malwarebytes' Anti-Malware checked. Then click on the Finish button.
MBAM will now automatically start and you will see a message stating that you should update the program before performing a scan. As MBAM will automatically update itself after the install, you can press the OK button to close that box and you will now be at the main program as shown below.


On the Scanner tab, make sure the the Perform full scan option is selected and then click on the Scan button to start scanning your computer for infections.
MBAM will now start scanning your computer for malware. This process can take quite a while, so I suggest you go and do something else and periodically check on the status of the scan.
When it's finished click on the Remove Selected button to remove all the listed malware. MBAM will now delete all of the files and registry keys and add them to the programs quarantine. When removing the files, MBAM may require a reboot in order to remove some of them. If it displays a message stating that it needs to reboot, please allow it to do so.
Combofix (Double Click on JeniP.com on your desktop)
ComboFix will now install itself on to your computer. When it is done, a blue screen will appear as shown below.

It will then back up the registry and ask if you want to installl the recovery console. Press yes


Once its done press yes again and you should see the following sequence





Tdskiller
Extract and Execute TDSSkiller.exe
Press Start Scan
If malicious software was found then make sure cure is selected. If there is no option to 'Cure' its critical that you select skip.
Click continue ->Reboot now
MGtools
Just double click on the mgtools.exe and let it run
When your done you need to enable UAC again.
Navigate into the \\MGTools folder just created in the root of your Windows boot drive.
*.locate the EnableUAC.reg file and double click on it and allow it to be added to the registry.
*.This registry patch is used to enable the User Account Control feature
*.You should reboot after applying the registry patch so that it works properly.
When that is done disable system Restore and enable it again.
For Windows 7
1. Click Start
2. Right click Computer > Properties > Choose Advanced System Settings option in left menu listing.
3. Click System Protection tab
4. Then highlight the drive you wish to turn off System Restore and click Configure
5. Then choose Turn off system protection
6. Click Apply > OK
Reboot
To re-enable follow steps 1 - 4 and then choose Restore system settings and previous versions of files > Apply and OK
For Vista
1. Click Start
2. Right click Computer > Properties > Choose Advanced System Settings option in left menu listing.
3. If UAC enabled you will get a UAC prompt at this click Continue
4. Click System Protection tab
5. Then Untick any Drive Listed and in the popup window click Turn Off System Restore
6. Click Apply > OK
7. Reboot
To enable repeat the above steps
Run Ccleaner once.
Remember to save all the applications you download on another spot as OTL is going to remove them and clean up the pc.
To cleanup download OTLcleaner
Click on the Green Clean Up button
If your still having issues upload the mgtools.zip folder. It contains all the logs of the applications above.
To help with not getting infected again or better pc security follow these guide lines.
System Repair
To repair any damage done by malware use Virus Effect Remover.
It is a repair tool Assists end-users to remove the effects, of either a live virus or left over by a virus (or trojan,) in most Windows® Operating Systems W98SE/WinXP/Win2K-All/Vista & Win7.
Repairs and fixes OS items such as : Taskmanager, Regeditor, MSconfig, Folder Options.

WINDOWS UPDATES
Keeping Windows up-to-date is your best bet in keeping your computer safe and secure. The second Tuesday of every month is known as Patch Tuesday. This is the day that Microsoft releases monthly hotfixes and service packs for software installed on your computer. Be sure you have the latest service pack, hotfix rollup, and/or updates installed on your computer. These patches resolve known issues and other bugs that would put your computer at risk.
It is recommended to use Microsoft Update to get updates for both Windows and other Microsoft software such as Office.
Recommended settings for Automatic Updates are
*. Automatic (Recommended)
*. Every day at 5:00 PM
You should not install any drivers from Windows Update, always get them from the manufacturer.
For those on a highspeed connection and having multiple computers in their homes, here is a wonderful application called WSUS
WSUS Offline Update downloads updates for Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Microsoft Office 2003/2007. It then creates an ISO for a CD/DVD that you can use to update computers without an Internet connection. This is a great tool for technicians and can also be easy to use for most users too.
ANTIVIRUS
Avira AntiVir Personal Edition is very light on resources and the detection rate of malware is outstanding, better than almost every other antivirus according to tests. However, there are some minor reservations.
First, AntiVir does not include web or e-mail scanning capabilities; this is only available in the paid version. The lack of an e-mail scanner is not really a disadvantage , it just means that AntiVir won't warn you of infected emails before you open them. But should you open an infected email, AntiVir will still spring into action, so it doesn't mean that you're not protected from email-based infections. Although AntiVir had signature updating problems in the past, this issue seems to be fixed now.
Avast! Free Antivirus is also an excellent free antivirus that is very popular. The antivirus detection rates is on par with AntiVir and Microsoft Security Essentials. Avast has the most features, with full real-time capabilities, including web, e-mail, IM, P2P and network shields, boot-time scanning, and a behavioural blocker. Avast is also light on resources. The newly released version 6 brings even more features including an internet site ratings plugin, script malware protection and a limited (non-configurable) sandboxing feature.
Security Essentials 4.1.522 Vista got good detection rates, particularly for rootkits. Even more impressive is that Security Essentials has very few false positives, is light on resources and is good at removal of existing malware.
Microsoft Security Essentials is a great choice for average users because of the minimal user interaction required. It automatically updates and removes threats. No registration is needed, apart from a quick validating of Windows, and there are no nag screens or advertisements.
The main downsides are the slow scan speeds and the lengthy amount of time it takes to quarantine malware. MSE also is not available in certain countries so users there will have to look elsewhere. Note that Microsoft Security Essentials requires a genuine copy of Windows to install.
Panda Cloud Antivirus is Panda's successful attempt to jump on the free antivirus bandwagon. With a simple interface and completely automated features with automatic updating and removal of malware, it is an excellent choice for average users. The detection level is generally very high, but detection of zero day threats is slightly lower. PAC has a behavioural blocker and web protection, which will certainly increase your security, however I will only compare the AV component as you can simply use one of the other free AV's with a separate behavioural blocker
Comodo Internet Security is the free, multi-layered security application that keeps hackers out and personal information in.
Built from the ground upwards with your security in mind, Internet Security offers 360° protection by combining powerful Antivirus protection, an enterprise class packet filtering firewall, advanced host intrusion prevention and automatic sandboxing of unknown files.
Unlike the stripped down versions of commercial software that other software vendors offer for free, this is the full, completely functional version of the product.
Internet Security Includes:
Antivirus: Tracks down and destroy any existing malware hiding in a PC.
Anti-Spyware: Detects spyware threats and destroys each infection.
Anti-Rootkit: Scans, detects & removes rootkits on your computer.
Bot Protection: Prevents malicious software turning your PC into a zombie.
Defense+: Protects critical system files and blocks malware before it installs.
Auto Sandbox Technology™: Runs unknown files in an isolated environment where they can cause no damage.
Memory Firewall: Cutting-edge protection against sophisticated buffer overflow attacks.
Anti-Malware Kills malicious processes before they can do harm.
Second Opinion Scanners
Hitman Pro - If your child is not feeling well and you suspect he or she has a virus infection you're going to visit your doctor. But what do you do when the doctor tells you that he cannot find anything but your child still does not feel very well? Of course, you go to visit another doctor for a second opinion.
This is the same what Hitman Pro does for your computer. Hitman Pro is a second opinion scanner, designed to rescue your computer from malware (viruses, trojans, rootkits, etc.) that have infected your computer despite all the security measures you have taken (such as anti virus software, firewalls, etc.).
Hitman Pro is designed to work alongside existing security programs without any conflicts. It scans the computer quickly (less than 5 minutes) and does not slow down the computer (except for the few minutes it is scanning). Hitman Pro does not need to be installed. It can be run straight from a USB flash drive, a CD/DVD, local or network attached hard drive.
Computer users can use the Free Scan of Hitman Pro as a quick check (less than 5 minutes) to ensure that the existing anti virus program has not missed a threat.
Help Desk and Support organizations can use the Free Scan of Hitman Pro as a quick check for viruses and other malware. It can be run from USB or CD/DVD. No installation is required.
Website owners can offer the Free Scan of Hitman Pro as a service to visitors for a quick second opinion.
Hitman Pro offers you a Free Scan for a second opinion. It is designed to check if your security measures work. If nothing is found (and we sincerely hope so), then you will never need a license. When a virus is found, then you will receive a free 30-day license to remove the threat.
FIREWALLS
What is a network firewall?
A firewall is a system or group of systems that enforces an access control policy between two networks. The actual means by which this is accomplished varies widely, but in principle, the firewall can be thought of as a pair of mechanisms: one which exists to block traffic, and the other which exists to permit traffic. Some firewalls place a greater emphasis on blocking traffic, while others emphasize permitting traffic. Probably the most important thing to recognize about a firewall is that it implements an access control policy. If you don't have a good idea of what kind of access you want to allow or to deny, a firewall really won't help you. It's also important to recognize that the firewall's configuration, because it is a mechanism for enforcing policy, imposes its policy on everything behind it. Administrators for firewalls managing the connectivity for a large number of hosts therefore have a heavy responsibility.
What can a firewall protect against?
Some firewalls permit only email traffic through them, thereby protecting the network against any attacks other than attacks against the email service. Other firewalls provide less strict protections, and block services that are known to be problems.
Generally, firewalls are configured to protect against unauthenticated interactive logins from the "outside'' world. This, more than anything, helps prevent vandals from logging into machines on your network. More elaborate firewalls block traffic from the outside to the inside, but permit users on the inside to communicate freely with the outside. The firewall can protect you against any type of network-borne attack if you unplug it.
Firewalls are also important since they can provide a single "choke point'' where security and audit can be imposed. Unlike in a situation where a computer system is being attacked by someone dialing in with a modem, the firewall can act as an effective "phone tap'' and tracing tool. Firewalls provide an important logging and auditing function; often they provide summaries to the administrator about what kinds and amount of traffic passed through it, how many attempts there were to break into it, etc.
This is an important point: providing this "choke point'' can serve the same purpose on your network as a guarded gate can for your site's physical premises. That means anytime you have a change in "zones'' or levels of sensitivity, such a checkpoint is appropriate. A company rarely has only an outside gate and no receptionist or security staff to check badges on the way in. If there are layers of security on your site, it's reasonable to expect layers of security on your network.
Proactive firewalls have the most extended protection, including HIPS or program monitoring (HIPS Explained), and watch for malicious behavior before malware gets a chance to take control of your PC or turn it into a botnet drone. They seek to achieve stronger "2-way" protection, preventing programs from broadcasting your personal information to the Internet.
Some kinds of malware are best detected by their behavior, so a proactive firewall (or firewall/HIPS combo) is a solid second layer of protection next to your antivirus program. It's an excellent option for high risk users.
The built-in Windows firewall is a common choice since it passes all inbound tests (both stealth and open port) and doesn't have many popup alerts. It doesn't require installation, so it's not likely to conflict with your other programs. And many average users wouldn't reliably handle the popup alerts of the best firewalls on the market (especially at their max settings).
If you scan clean for malware and you don't want the features of a third-party firewall, then the Windows firewall is a practical and useful solution.
You can replace the Windows firewall with a basic third-party firewall for easier control of outbound protection and additional features. Most simple two-way firewalls ask you to allow or deny Internet access for unknown programs. Many automatically allow trustworthy apps and remember your decisions to become silent over time.
What can't a firewall protect against?
Firewalls can't protect against attacks that don't go through the firewall. Many corporations that connect to the Internet are very concerned about proprietary data leaking out of the company through that route. Unfortunately for those concerned, a magnetic tape can just as effectively be used to export data. Many organizations that are terrified (at a management level) of Internet connections have no coherent policy about how dial-in access via modems should be protected. It's silly to build a 6-foot thick steel door when you live in a wooden house, but there are a lot of organizations out there buying expensive firewalls and neglecting the numerous other back-doors into their network. For a firewall to work, it must be a part of a consistent overall organizational security architecture. Firewall policies must be realistic and reflect the level of security in the entire network. For example, a site with top secret or classified data doesn't need a firewall at all: they shouldn't be hooking up to the Internet in the first place, or the systems with the really secret data should be isolated from the rest of the corporate network.
Another thing a firewall can't really protect you against is traitors or idiots inside your network. While an industrial spy might export information through your firewall, he's just as likely to export it through a telephone, FAX machine, or floppy disk. Floppy disks are a far more likely means for information to leak from your organization than a firewall! Firewalls also cannot protect you against stupidity. Users who reveal sensitive information over the telephone are good targets for social engineering; an attacker may be able to break into your network by completely bypassing your firewall, if he can find a "helpful'' employee inside who can be fooled into giving access to a modem pool. Before deciding this isn't a problem in your organization, ask yourself how much trouble a contractor has getting logged into the network or how much difficulty a user who forgot his password has getting it reset. If the people on the help desk believe that every call is internal, you have a problem.
Lastly, firewalls can't protect against tunneling over most application protocols to trojaned or poorly written clients. There are no magic bullets and a firewall is not an excuse to not implement software controls on internal networks or ignore host security on servers. Tunneling "bad'' things over HTTP, SMTP, and other protocols is quite simple and trivially demonstrated. Security isn't "fire and forget''.
How can I test my firewall?
To test your firewall's ability to protect against incoming attacks and scans, visit one or more of the following sites. Note that if you are using a router, the test will target the router, not any software firewall your PC is running.
Shields UP!
PCFlank
Sygate Online Scan
HackerWhacker
Please note that while your firewall may report these scans as an "attack", you should not report this to any ISP. The Outpost Online Scans - What to do with Open and Closed Ports has more information about what the results mean and what action to take.
Outpost Security Suite Free Provides antivirus and firewall protection from both inbound and outbound attacks and is also much easier on the user when gaming or using fullscreen applications. If you already have one of the above anti-virus solutions Outpost will automatically detect this and disable/not install their anti-virus.
Online Armor Personal Firewall 's RunSafer is another option which I really like. It is very easy to use; you just select a program and click "Run Safer" and the program will now run with with restricted priviledges.
ZoneAlarm Free 10.2.078.000 is an excellent inbound/outbound OS firewall solution suited for users of every level of experience. ZoneAlarm protects systems from intrusions as well as program access to the web. ZoneAlarm features an easy-to-understand user interface. Users can adjust security settings for their needs to allow for file/printer sharing, public networks, and even turn off the firewall if ever needed. Simple controls in the form of visual slide bars make setting up this firewall a snap. ZoneAlarm offers to help users setup initial program access with a first-run scan of installed software and allows/denies accordingly. This first scan does not always offer accurate access to programs.
Users will have to interact with this firewall for a time after installation to make sure programs needing LAN or internet access are granted proper permissions. Pop ups are very simple in format offering Deny, Accept,and a checkbox a user can check to make ZoneAlarm remember the decision. Novice users should be able to easily identify the name of the program asking for web access so they can make the appropriate decision.
The Program Control will allow users to set ZoneAlarm for Low, which is a learning mode and no OS firewall protection and limited pop ups. Or users can choose Medium, which will make programs ask for permission to access the trusted and internet zones. The high setting is not offered in the Free version of ZoneAlarm. The Smart Defense Advisor will help reduce pop ups by offering settings for programs asking for access, based on the decisions made by other users worldwide. Users can choose whether or not to participate in ZoneAlarm's community defense program. Users can set programs access manually at anytime by going to ZoneAlarm's Program Control and selecting Programs.
Internet Zone controls are divided into the Trusted Zone, used for the local network to share files, printers, etc., and the Internet Zone for communication to/from the web. A simple 3-position format allows users to choose from "No protection" (firewall is off), Medium (Allows file/printer sharing), and High (will allow users to connect to a network but will not allow anyone else to connect to your system). The medium setting is recommended for home networks with more than one system, and for users whose modem requires this setting. The high setting is most recommended for single-system web access (only one computer at home and modem does not require a home network setting), and for public areas such as cafes, restaurants, and hotels (etc.) with wifi.
ZoneAlarm Free offers basic two-way defense, stealth mode, and anti-phishing protection. However, it lacks HIPS or program-to-program protection.
You can go HERE for a very good guide setting up a firewall.
Look 'n' Stop: a Lightweight and Effective Personal Firewall
Look 'n' Stop Firewall has been around for years; it's a solid protect that provides excellent protection and is extremely light on resources.
32-bit and 64-bit editions of Windows are supported by Look 'n' Stop (LnS): Windows 7, Vista, XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows 2000, ME and 98. The Visual C++ Runtime Library is also required but you do not need to hunt for this required file because the installer will download and install it, if it detected missing.
Key Features of Look’n’Stop
Application Filtering LnS will alert you on any application that will use internet connection
Internet Filtering most firewall offer this feature to block or allow inbound and outbound data packets
Rule-based firewall you can create or modify new firewall rules
Advanced logging a neat feature in LnS is to have a log (simple or full logs) for any application of your choice. This is useful if you would like to monitor few or all applications network connections.
Plug-ins an option to extend the capability of Look n Stop firewall by activating available plug-ins
Look 'n' Stop includes an anti-flood log protection
The setup file is a small one mega-bytes file. It is extremely fast to download and to install, whatever Internet connection speed.
Available in 18 languages, Look 'n' Stop Firewall 2.07 is the most recent version of Look 'n' Stop Firewall, a reference firewall used world-wide since 2000.
Passwords
With the constant media bombardment about viruses, worms, hacking and crackers you’d be forgiven for believing that you shouldn’t touch the Internet with a ten footpole for fear of someone stealing your identity and running off with your life savings. But behind the news headlines and hype there is little more threat of that in the online world than there is from the risks of everyday theft or fraud. It is simply a matter of taking some simple precautions to protect yourself as you would when walking down the street or locking the house.
In these days of high speed "always on" broadband Internet connections the security of your of computer, files and privacy should be a priority. Unfortunately, a lot of people are leaving their virtual front doors unlocked, and giving crackers the green light to do as they wish, simply because they do not understand the risks and take the appropriate precautions.
The responsibility for this common lack of security falls squarely on the shoulders of the humble Windows operating system. The consumer versions of Windows 95, 98 and Me are based on code written back in the days before networks and modems became common, and certainly before computer security became the issue it is now. In fact the original foundations of Windows are based on MS-DOS 1.0 released back in 1981, and although obviously major improvements have been added since that time, the legacy of an insecure operating system remains.
So how do I create a strong password and make my OS a bit more secure?
Use 10 or more characters
Choose a combination of:
numbers
upper case letters
lower case letters
special characters such as ! $ * % @ # & -
(in some cases restrictions may apply )
Avoid passwords that are easy to guess or to crack
Dictionary words (mackerel, dandelion, millionaire)
Foreign words (octobre, gesundheit, sayonara)
Simple transformations of words (tiny8, 7eleven, dude!)
Names, doubled names, first name and last initial (mabell, kittykitty, marissab)
Uppercase or lowercase words (MAGAZINE, licorice)
An alphabet sequence (lmnop) or a keyboard sequence (ghjkl

Words that have the vowels removed (sbtrctn, cntrlntllgnc)
Easy ways to create and remember strong passwords
Use lines from a childhood verse:
Jack be nimble, Jack be quick = JbeN#jbq1
Use an expression inspired by the name of a city:
I love Paris in the springtime = 1LpntST!
Chicago is my kind of town = C1mYK0t
Use lines from a favorite song:
You can't always get what you want = uC4n+agwUw!
Change passwords every 6 months at least.
Change "first-time" passwords that are issued to you immediately.
Don't reuse old passwords.
Don't use the same passwords for work accounts that you do for personal accounts.
Whenever practical use unique passwords for all accounts
Don't write passwords down and leave them in places not always under your control.
Replace your passwords every 30 to 120 days.
Disable logon after a specified number of failed attempts.
Use SSH or SSL for remote server authentication.
Don't use programs that send passwords in plain text such as Samba, FTP,
Telnet, Pathworks V 4.0.
Don't use shared usernames and passwords.
Change or disable the common user names such as Guest and Administrator.
Log on at the lowest level needed for the work to be done.
Disable or remove unused accounts.
Securing Your Browser
Securing your browser is a great asset in protecting your computer. By properly securing your browser, you can stop all kinds of malware from getting in.
My first recommendation for safe browsing is a free program called Sandboxie , for Windows 2000 and later. It creates a special contained "sandbox" environment on your PC. While browsing within the virtual sandbox provided by Sandboxie, you are totally isolated from the vital portions of your PC, namely your operating system environment on your hard drive and memory locations for your current OS session. So any files you download are isolated to the sandbox. Similarly, any programs that are executed only do so within the sandbox, and*have no access to your normal files, the Windows operating system or any other part of your PC.
Usage is remarkably simple. To start a sandboxed browsing session, you just click the "Sandboxed Web Browser" icon on your desktop (or the Sandboxie icon from the Quick Launch tray) and this will launch your default browser in the sandbox. You can then use it in the normal way to browse to sites or download files. By default, files that are saved in the Desktop, My Documents or Favorites will have a prompt to ask you whether you want to save the file permanently. I suggest you add your default downloads folder to the Quick Recovery settings so files saved there will be automatically saved to your real hard disk, saving you the trouble of manually recovering files.
After you have finished browsing, you can right click the Sandboxie icon and delete all sandboxed files and processes, and your PC will be returned to the same state it was in before the browsing session. You can change configuration settings to automatically delete all the sandboxed contents when you close a sandbox. You can also configure a third-party program, such as Eraser or SDelete, to erase the sandboxed contents for greater privacy.
The advantage is clear: any virus, trojan, worm, spyware or adware threats that"infected" your PC while browsing will be eliminated.
Sandboxie allows for in-depth configuration which increases security. For example, you can set it to block access to your personal files, or only allow certain programs to run or connect to the internet in a sandbox. A recent feature of Sandboxie also allows you to run sandboxed programs in a Limited User Account , similar to DropMyRights, for even greater security. This should also prevent most keyloggers from running.
However, there are some downsides to this approach. Firstly, if you want to update your browser addons/widgets, you'll need to open an un-sandboxed browser and do it from there. This also applies to bookmarks but you can configure Sandboxie to automatically retain those. Secondly, Sandboxie is not designed to detect or disable keyloggers . You can get around this (mostly) by always empty your sandbox before you log in to important sites (such as sites involving financial transactions). Thirdly, some people find the nag screen inconvenient, which appears for five seconds before a sandboxed application opens.
Sandboxie works fine with all browsers and most software applications, including e-mail clients (though this requires special configuration ), instant messaging clients, Bittorrent clients and games. However, it won't work with system software (software which installs a system driver).
GesWall is another excellent option. It automatically isolates certain applications (browsers, PDF viewers and file archivers) as well as files, registry keys, processes made by those applications. The generic rules for an isolated application are that the application:
1. Can read but cannot modify trusted resources.
2. Cannot read or modify confidential resources.
3. May create new untrusted resources, e.g. files.
4. May read or modify untrusted resources.
Known applications also have pre configured rules so those applications can run properly.
In effect, files which you download will not be able to access critical areas on your computer, similar to a Limited User Account. So any malware which you in adverdently download cannot execute and damage your computer. GesWall also allows for detailed customization where you can configure the restrictions of untrusted applications.
Overall, GesWall provides excellent security, and is a worthy alternative to Sandboxie.
KeyScrambler - Using advanced encryption algorithms, KeyScrambler encrypts your keystrokes deep in the kernel, as soon as they enter the computer.
When the encrypted keystrokes finally arrive at the intended application, the decryption component of KeyScrambler goes to work, and you see exactly the keys you've typed.
This way, as your keystrokes go through the different layers of the operating system, it doesn't matter if they get logged, or whether the keyloggers are known or brand new, because your keystrokes are completely indecipherable the whole time.
If you're up for it, consider making LastPass your easy, any-browser, any-OS solution , or get into KeePass for even tighter, more customized security.
Not up for installing something new and setting it all up? Then simply fix up your current browser's password-saving system.
Firefox can save your passwords, but does so insecurely, so that anyone who grabs your laptop, or digs into your files, can read them. So be sure to enable the Master Password , and while you're at it, install Master Password for a less-annoying, more-secure tool.
Chrome can save your passwords, too, and also sync them through the Google cloud to any other Chrome browser you use. But be sure to protect your passwords with a pass phrase .
Internet Explorer , even in its pre-release ninth version, doesn't offer much in the way of password protection, beyond a toggle to ask you before saving each password. You're best off getting friendly with LastPass .
Enable HTTPS and Better Security Everywhere You Can
If you're surfing without an encrypted connection, you're leaving yourself open to, at best, a practical joke from friends; at worst, a breach of security in your social networks, email, or other accounts, which can lead to further harm. It seems like paranoia, unless you've had a tech-savvy friend prove to you just how open you are.
Most sites that you'd want to use now offer an encrypted connection option, usually termed as "HTTPS" or "SSL". If a site doesn't have that option, and it's holding your personal data, consider whether you really need to be using that service. Here are the services for which you should definitely enable the secure/https option:
Gmail
Secure connections are usually a default now, but double-check: head into Settings, look under "Browser connection," and ensure that "Always use https" is enabled. (Be sure, too, that you've enabled two-step verification for your Google account , Gmail included.
Recently offered , and not enabled by default. To make use of it, click the Account link on any Facebook page while logged in, head to Account Settings , then, under "Account Security", hit the change button and check the box that says"Browse Facebook on a secure connection (https) whenever possible." Hit the Save button and head elsewhere.
Yahoo
Yahoo has a lot of really great, personalized account security options so why aren't you using them? Logged into any Yahoo page, click under your name (in the "Hi NAME" link), and choose Account Info. You'll have to enter your password again (but, hey, that's good!), but then you can set custom password reset questions, require an SMS code for verification, set up an alternate email address for account recovery, and many more really good options that are both free and easy to use.
Hotmail
Now offered for everyone, though not fully supported across clients like Outlook and Windows Live Mail. If you're mostly using Hotmail in your browser, add an "s" to your Hotmail URL (https://hotmail.com), and you should see a screen asking you if you always want to use a secure connection. You probably do.
eBay/PayPal
Log into PayPal, click the My Account tab, then click the Profile sub-tab. Look for the "Security Key" tab. For $5, you can order a passphrase that arrives in physical form, and without which PayPal won't let anyone come close to your money. For those who do a decent amount of trading, especially overseas, it's a worthy investment.
Take a tip from Jeff Atwood, who found that, despite his best intentions, he had a fake anti-virus app installed on his machine. The culprit was a Java plug-in that allowed a site Atwood was passing by to sneak in some badly behaved code.
First things first: head to Mozilla's super-handy Plugin Check page , which works with almost any browser, and see which of your plug-ins need updating now. You'll probably be a bit surprised, as even I was.
Chrome has a few good options for keeping insecure plug-ins at bay. You can set them to "click-to-play" or disable them indivually , or enter about:flags into your address bar and enable the "Disable outdated plugins" option to automatically shut down plug-ins that have known vulnerabilities.
Firefox will work some automatic plug-in monitoring into its future versions, as will other browsers; for now, consider making Plugin Check something you visit frequently maybe even as one of your multiple startup pages.
SpywareBlaster 4.6 - This excellent product will protect both Internet Explorer and Firefox. Unfortunately it does not cover Opera.
SpywareBlaster adds a large list of malicious websites to Internet Explorer's Restricted Sites list. It also restricts malicious ActiveX components and ad/tracking cookies. The Firefox protection also blocks ad/tracking cookies.
EULAlyzer
One risk too many people take with software is not reading the End User License Agreement. This is understandable as many agreements are long and complicated. The problem is you may be exposing yourself or your machine to undesirable conditions. There aren't any shortcuts to the review process, but there is a free EULA analyzer software package that can flag interesting items for you in software license agreements or privacy policies.
If you're not familiar with the term EULA, it's an acronym for End User License Agreement. It's a contract you and the software provider enter which covers items ranging from copyrights to liabilities. Because of their complexity, many people accept the agreements without reading them. They want to believe there is nothing bad in the agreement, or in the software.
Some years back, it may have been safe to blindly accept the agreements. Today, more software packages or services infringe on your privacy or may use your PC and bandwidth. Others packages are categorized as ad-sponsored, which often contain clauses about serving advertisements or installing third party items. The result is we may be giving in or giving up in ways we didn't anticipate.
At first, I was a skeptical when I read about EULAlyzer program. After all, how well can a program interpret the terms we see in these software agreements? Then I noticed the same people who created SpyWare Blaster, which is a great tool, publishes EULAlyzer. It then occurred to me that Javacool Software was nicely suited for this task since they see many instances of how spyware and malware are embedded into software and the wording used in those software agreements.
As with their other programs, EULAlyzer is easy to use and provides a fast way to grab and copy a EULA or privacy policy. This involves dragging the programs + icon over the license agreement you'd like to review. The contents are then pasted into EULAlyzer. In some cases, such as web pages, you may have to do a copy and paste.
Spybot S&D Immunize - Adds a large list of malicious websites to Internet Explorer's Restricted Sites list just as SpywareBlaster does. This can be found by clicking the Immunize button on the left side of Spybot Search & Destroy 2.0 RC2.
Web of Trust (WOT) - A free Internet security addon for your browser. It will keep you safe from online scams, identity theft, spyware, spam, viruses and unreliable shopping sites. WOT warns you before you interact with a risky website. This addon makes use of the OpenDNS project titled Phishtank to help detect bad websites. WOT is available as an add-on for Internet Explorer, and Mozilla Firefox and as a bookmarklet for Opera, Google Chrome, Safari, and any other browser supporting Javascript and bookmarks/favorites. After downloading the addon to the user's browser, the WOT logo appears in the web browser's navigation toolbar. When the user navigates to a website, the color of the logo will change color based on a traffic light system (Green, Light Green, Yellow, Light Red or Red); depending on the reputation of a website determined by its users.
SAFER INTERNET
You can add a layer of protection to your home network or computer by using OpenDNS
Many routers support adding OpenDNS in an easy to configure manner as well as several open-source firmwares. One such firmware is the Tomato firmware which is most commonly used on the WRT54GL router.
OpenDNS can help to filter out bad websites that contain adware and phishing attempts. It makes use of PhishTank which is a community based anti-phishing service. PhishTank is used by Opera, WOT, Yahoo Mail and by PhishTank Site Checker.
Its easy to setup. Go HERE for a guide to set it up
An account with OpenDNS is not required, it is recommended. Best of all it's free. Having an account allows you to filter out all types of websites.
Norton DNS uses Symantecs exhaustive Safe Web database. This is the database that underpins most of Symantecs security efforts, and brings together the results of its anti-malware research, anti-spam efforts and many more. Non-commercial efforts like malwaredomains.com, while highly useful and accurate, simply won¡¯t be able to compete with the volume of information Safe Web offers.
Currently it is free for non-commercial use, and takes nothing more than pointing your DNS client at the servers.
Currently 198.153.192.1 and 198.153.194.1
If you prefer not to muck about with network settings, Symantec has provided client software for both Windows and OSX. The client software acts as a local DNS repeater allowing you to bypass restrictions that may exist in using off-network DNS providers.
Comodo Secure DNS is a domain name resolution service that resolves your DNS requests through our worldwide network of redundant DNS servers. This can provide a much faster and more reliable Internet browsing experience than using the DNS servers provided by your ISP and does not require any hardware or software installation.
As a leading provider of computer security solutions, Comodo is keenly aware of the dangers that plague the Internet today. SecureDNS helps users keep safe online with its malware domain filtering feature. SecureDNS references a real-time block list (RBL) of harmful websites (i.e. phishing sites, malware sites, spyware sites, excessive advertising sites, etc.) and will warn you whenever you attempt to access a site containing potentially threatening content. Additionally, our 'name cache invalidation' solution signals the Comodo Secure DNS recursive servers whenever a DNS record is updated - fundamentally eliminating the concept of a TTL. Directing your requests through highly secure servers can also reduce your exposure to the DNS Cache Poisoning attacks that may affect everybody else using your ISP.
It's quick and easy to change to Comodo Secure DNS. No downloads and it's absolutely free.
156.154.70.22
156.154.71.22
No OS is safe. Not even Industrial systems.
Here is Nortons Dossier on Stuxnet
Malware Lingo
Adware
Adware is any type of advertising-supported software that will play, display, or download advertisements automatically on a user's computer once the software hasbeen installed on it or while the application is in use. Some adware can alsobe spyware due to its privacy-invasive characteristics.
BackDoor
A backdoor in a computer system (or cryptosystem or algorithm) is a means of circumventing regular authentication, securing remote computer access, accessing plain text, etc., while remaining to be undetected. A backdoor may appear to be an installed program or a modification to a program or hardware device that's already installed.
Baiting
Baiting uses tangible media and relies on the curiosity or greed of the victim. Baiting involves an attacker leaving a malware infected media such as a CD ROM or USB flash drive in a public place where it is likely to be found, appearing to be legitimate and appealing, and waits to be used by the victim. Baiting is easy to perform as in this example where an attacker might create a malware loaded CD with a company logo on it, and the words"Company Reorganization Plan" on the front. The media is left on the lobby floor ofthe targeted company. An employee could find it and then insert it into a computer to satisfy their curiosity. By inserting the CD into a computer to view its contents, the user unknowingly installs malware on it, allowing the attacker access to his computer and possibly, the company's computer network. If there is no mechanism to block the malware, then computers set to "auto-run" inserted media could be immediately compromised when the CD is inserted.
Botnet
Botnet is a collection of software robots, or bots, that are automatic and self-directed. Botnet is often associated with malware but can refer to the network of computers using distributed computing software.
Botnet generally refers to a group of compromised computers called zombie computers running software that is usually installed via worms, trojans or backdoors, under a common command-and-control infrastructure.
Browser plugin
A browser plugin is a software program that extends the capabilities of your Internet browser in a specific way. Not all browser plugins are harmful and some maybe helpful. This category contains mostly dubious browser plugins such as "Search Assistant", toolbars, etc. that have been known to transmit user data to their creators or have been installed using covert means.
Commercial Network
A commercial network management tool is mostly used in (large) corporations. It can log the network traffic passively (sniffing) or examine the logs of proxies, etc. Nothing is installed on the individual computers, the software runs on a central server. They can only log items that pass through the network, but not local items such as the entered passwords, keystrokes or screenshots.
Crimeware
Crimeware is a distinct type of malware designed to automate financial crime by performing identity theft to access online accounts of users at financial institutions and online retailers for the express purposeof stealing funds from those accounts or performing unauthorized transactions to the benefit of the thief controlling the crimeware. Crimeware is often used to export private information from a network for financial exploitation. Crimeware is viewed as a growing concern in network security as this type of threat seeks to steal confidential information.
Computer virus
A computer virus is computer software that has the ability to replicate itself and infect a computer without the informed consent or knowledge of the computer user. Certain malware, adware and spyware have been incorrectly termed as a virus because they lack the ability to copy themselves. A real virus spreads from one system to another through an executable code when its host is transferred to a target computer; such as being sent over a network or the Internet, email or transported via removable media such as a CD, DVD or USB drive. Infected files residing in a network file system or any instance where a computer can be accessed by another one increases the chances of spreading a virus infection.
The term "computer virus" is considered to be malware, a much broader term which also encompasses several types of malicious software including worms, trojans, and others. Although technically different, viruses are often confused with computer worms and trojans. Unlike a virus, a worm can take advantage of security holes in order to spread itself among other systems, while a trojan appears to be harmless but has an underlying plan. A worm, trojan or virus, once executed, can endanger a computers data, operation, or network ability. User awareness of some computer viruses and other malware may be readily apparent while many other types go unnoticed.
The increasing number of computers being connected to local area networks and the Internet is creating an environment for computer viruses to spread. Increased use of email and instant messaging are additional ways computer viruses spread.
Computer worm
A computer worm is a self-replicating computer program that sends copies of itself within a computer network and it can do so without any involvement by the user. A worm doesn't need to attach itself to an existing program in order to spread. Worms typically cause some harm to the network, most notably by consuming bandwidth.
Data miner
A data miner's primary function is to gather data about an end user. Some adware applications may employ data mining abilities.
Email bomb
An email bomb is a form of network abuse by sending enormous amounts of emails toan address in an attempt to overflow the mailbox or overwhelm the mail server where the email address is hosted in what is called a denial-of-service attack.
Email spoofing
Email spoofing is a fraudulent email activity in which parts of the email header and the sender address are modified, appearing as if the email was sent from another source. This technique is commonly used for spamming and phishing to conceal the origin of an email message. By altering certain properties of the email header, such as the From, Return-Path and Reply-To fields, fraudulent users can make the email appear to have been sent from someone other than the real sender.
Sometimes the source of the spam email is indicated in the Reply-To field. If the initial email is replied to, it will be delivered to the address specified in the Reply-To field, which might be the spammer's address. But most spam emails, especially malevolent ones carrying a trojan or virus, or those advertising a website, falsify this email address, sending the reply to another potential victim.
Exploit
An exploit is a portion of software, data, or string of commands that take advantage ofa computer bug, glitch or vulnerability disrupting normal behavior on computer software, hardware or other electronic device. Usually this includes seizing controlof a user's computer system or attacks that allow privilege escalation or a denial of service.
Fast flux
Fast flux, DNS technique, is used by botnets to conceal phishing and malware distribution sites behind a continuously changing network of compromised host systems utilized as proxies. Fast flux can also refer to a combined peer-to-peer network, distributed command and control, web-based load balancing and proxy redirection to make malware networks less detectable and more resistant to counter-measures.
Fast flux may be seen by Internet users in phishing attacks linked to crime organizations, including attacks on social networks.
Fraudulent dialers
Dialers are used to connect computers to the Internet but fraudulent dialers are designed to connect to premium-rate numbers. Fraudulent dialers are often installed through security holes in a computer's operating system and will change the computer settings to dial up through the premium-rate number. The additional monies are collected by the provider of the fraudulent number. Some dialers inform the user of benefits for usingthe special number to access special content which is usually illegal materials or downloads.
Users that have DSLs or other broadband connections are usually not affected since adial is dependent on regular phone lines. But, if an ISDN adapter or additional analogmodem is installed, the dialer may be able to connect.
Malicious dialers can be identified by:
A download popup opens when a website is opening.
The website may or may not discreetly display a price.
The download initiates even if the cancel button has been clicked.
Without any notice, the dialer installs as a default connection.
The dialer perpetuates unwanted connections without any user action.
No notice about the price is presented before dialing in.
While connected, the high price of the connection is not shown.
The dialer cannot be easily uninstalled if at all.
Hijacker
Hijacker is an application that attempts to take control of the user's homepage and replace it with one that the hijacker chooses. It is a low security threat, but is annoying. Most hijackers use stealth techniques or trick dialog boxes to perform installation.
Browser hijackers commonly do one or more of the following:
Change your "search" page and passes all searches to a pay-per-search site
Change your default home page to the company page. Sometimes the software changes them to a portal featuring porn sites.
May transmit URLs viewed toward the company server
Hoax
A hoax is an attempt to purposefully dupe an audience into believing something is real, when it actually is not what it appears or claims to be. A hoax can be made by using only true statements but with different context or wording. A hoax is often carried out as a practical joke, to cause embarrassment, or to create awareness to prompt social change. Many hoaxes are motivated to poke fun at, educate or point out the absurdity of the target.
Keylogger
A keylogger is surveillance software capable of recording all the keystrokes a user makes and saving that to a log file, which is usually encrypted. A keylogger recorder captures information entered on a keyboard including instant messages, email and any other type of information. Some keyloggers record email addresses the user uses and URLs that are visited. Thelog file created by the keylogger can then be sent to a designated receiver.
As a surveillance tool, keyloggers, are oftenused in the workplace by employers ensuring work computers used by employees are for business purposes only. However, keyloggers can be embedded in spyware allowing the user's information tobe sent to an unauthorized third party.
Loyaltyware
Loyaltyware is a sub-form of adware. Loyaltyware is a type of software that works around the concept of user loyalty by providing incentives in the form of cash,points, airline miles, or other type of goodswhile shopping.Loyaltyware
Malware
Malware, a term meaning "malicious software", refers to a set of computer instructions created for the express purpose of infiltrating a computer system, and modify, record, damage or transmit data without the permission of its owner. The term "malware" is generally used to describe any form of intrusive, hostile, or bothersome software application or code.
Malware covers a broad range of types, from cookies without consent used for tracking user surfing behavior, to more malevolent types such as viruses, worms, trojans, specific rootkits, spyware, adware,scareware, crimeware and other forms of malicious software. Certain government statutes define malware as a computer contaminant and is written into legal code in many states.
Parasiteware
Parasiteware is the term for any adware that by default overwrites certain affiliate tracking links. These tracking links are used by webmasters to sell products and tohelp fund websites. The controversy is centered on companies like WhenU, eBates,and Top Moxie, popular makers of adware applications. These companies release their software to assist users in getting credit for rebates, cash back shopping, or contributions to funds. To the end user, parasiteware represents little in the way of a security threat.
Phishing
Phishing is a criminally fraudulent process of collecting sensitive information such as usernames, passwords and credit card details by pretending to be a trustworthy entity in an electronic communication. Communications supposedly from well known social networks, auction sites, online payment processors or IT administrators are common fronts to bait the unsuspecting computer user. Phishing is commonly performed by email or instant messaging, directing users to enter details at a fake website that mimicks a legitimate one. Even when using server authentication, it may not be apparent that it is a fake website. An example of social engineering techniques, phishing is used to trick users, exploiting the weaknesses of web security technologies. The rising number of phishing scams has prompted and increase of legislation, training for the user, public awareness, and technical security procedures.
Pretexting
Pretexting is the practice of presenting on self as someone else for the purpose of acquiring sensitive information and is usually performed over the telephone. Presenting an invented scenario involves some prior research or using bits of known information such as data of birth or billing address to establish credibility with the targeted victim.
This method is often used in business to disclose customer information. Private investigators use this technique to acquire telephone, utility and bank records, and other information. This gives the investigator factual basis to establish legitimacy with managers of the business for even tougher questioning.
Many U.S. companies continue to use client verification by asking questions whose answers are supposedly known only by the client such as a Social Security Number or mother's maiden name, thus perpetuating this security problem even more.
Pretexting is also used to impersonate any individual who could be perceived by the targeted victim as have authority or right to know. The pretexter prepares answers that could potentially be asked by the targeted victim and must sound convincing to achieve his goal.
Rogue security software
Rogue security software uses malware or malevolent tools to advertise or install itself or forces computer users to pay to remove non existent malware. A trojan is often installed by rogue software when downloading a trial version, or it will run other unwanted actions. Rogue software makers want users to install and purchase their product. A common tactic to install their program, is to display fake Windows dialog boxes or other browser pop-up with messages that entice the user to click on them. Usually a message is displayed such as "WARNING! Your computer is infected with Spyware/Adware/Viruses! Buy [software name] to remove it!", another message is "Click OK to scan your system" without asking to buy the software. Yet another example is "Computer/Internet Connection/OS is not optimized and to Click Here to scan now".
Once the user clicks the OK button in the dialog box, he will be directed to a malicious website, which installs the program. Sometimes, clicking close window or X button in an attempt to close the dialog box will have the same effect. (To circumvent that trick, Press Alt F4 or use Ctrl-Alt-Delete to access the Task Manager). Some rogue software will download the trial version automatically without any user interaction. In addition to rogue programs being installed, many sites now use a technique to install multiple trojans at once by downloading a dropper first, loading various malware to the unsuspecting user's computer.
Rootkit
A rootkit is a software system containing one or more programs designed to show no indication that a system has been compromised. a rootkit is used to replace essential system executables, which can then conceal processes and files installed by the attacker as well as rootkit itself. A rootkit's intention is to control the operating system. Rootkits obscure their presence on the system through by evading standard operating system security mechanisms.
Rootkits can also be trojans, tricking the user into thinking they can be safely run on their systems. This can be achieved by concealing running processes from monitoring programs, or hiding files or system data from the operating system. Rootkits are also capable of installing a "back door" in a system by changing the login mechanism (such as /bin/login) with an executable that accepts a secret login combination, allowing the system to be accessed by an attacker, even if changes are made to the actual accounts on the system.
Originally, rootkits may have been normal applications, designed to take control of a faulty or unresponsive system, but more recently have been produced as malware allowing attackers to gain access to systems undetected. Rootkits exist for a variety of operating systems, such as Microsoft Windows, Linux, Mac OS, and Solaris. Rootkits often install themselves as drivers or kernel modules or modify parts of the operating system, depending on the internal elements of an operating system's mechanisms.
SMiShing
Smishing is a criminal activity that utilizes social engineering techniques similar to that of phishing. The name originated from"SMs phISHING". SMS or Short Message Service, is the technology behind text messaging on cell phones. Like phishing, smishing uses text messages on cell phones to lure a user into revealing personal information. The method used to actually "capture" user's information, or"hook", in the text message could be a website URL, although it is more typical that a phone number is displayed that connects to an automated voice response system.
Smurf attack
The Smurf attack is a means of producing a large amount of traffic on a computer network. This is a type of denial-of-service attack that overwhelms a target system via spoofed broadcast ping messages. In this case, an attacker sends a large volume of ICMP echo requests, or pings, to IP broadcast addresses, all having a spoofed source IP address of the targeted victim. If the routing device that delivers traffic to those broadcast addresses sends the IP broadcast to all the hosts, then many of the hosts on that IP network will take the ICMP echo request and send an echo reply, thus multiplying the traffic by the number of hosts that respond. Hundreds of machines on a multi-access broadcast network could reply to each packet.
Spamware
Spamware is software designed by or for use by spammers. Spamware can include the capability to import thousands of email addresses, generate random email addresses, insert fraudulent headers into messages, use multiple mail servers at once, and use open relays. Spamware can also be used to locate email addresses to build lists for spamming or to sell to spammers.
Spyware
Spyware is computer software that is installed on a user's computer without the user's express consent with the purpose of collecting information about the user, their computer or browsing habits.
As the term implies, spyware is software capable of secretly monitoring the user's behavior, but can also collect various types of personal information, including web surfing habits and websites visited.
Spyware can also impede the user's control of his computer by installing additional software, and redirecting web browser activity. Spyware is known to cause other interference by changing computer settings that slow connection speeds, load different home pages, and lose Internet connectivity or program functionality.
With the proliferation of spyware, an antispyware industry has sprung up. Use of antispyware software is now a widely accepted practice for the security of Microsoft Windows and desktop computers. A number of anti-spyware laws have been passed, targeting any software that is surreptitiously installed with the intent to control a user's computer. Due to its privacy-invasive characteristics, the US Federal Trade Commission has placed a page on their website advising consumers on how to lower the risk of being infected by spyware.
Trojan horse
The Trojan horse, or trojan, is a type of malware that appears to have a normal function but actually conceals malicious functions that it performs without authorized access to the host system. A Trojan can allow the ability to save their files on the user's computer or monitor theuser's screen and control his computer.
A trojan is not technically a virus but can be easily and unknowingly downloaded by the computer user. One example might be a computer game, when executed by the computer user, allows a hacker to control the user's computer. In this case the computer game is a trojan.
Vishing
Vishing is the unlawful practice of utilizing social engineering over the telephone system, using features of Voice over IP (VoIP) to access confidential personal and financial information from the public for financial reward. The term "vishing" is a combined form of "voice" and "phishing".
Vishing takes advantage of the public's trust in using landline telephone systems that end in physical locations recognized by the telephone company, and associated with a paying customer. VoIP makes previously anti-abuse tools or features of caller ID spoofing, complex automated systems (IVR), low cost, and anonymity for the paying customer widely available. Typically, vishing is used to capture credit card numbers or other sensitive information to be used in identity theft schemes by perpetrators.
Legal authorities find it difficult to monitor or trace vishing scams, although technology is used to monitor all PSTN based traffic, identifying vishing attempts as a result of patterns andanomalies in call activities. Consumers are advised to be suspicious when they receive messages prompting them to call and give their credit card or bank numbers. Usually, the consumer is directed to contact their bank or credit card company to verify the message.
VoIP spam
VoIP spam, is the proliferation of unwanted phone calls that are automatically-dialed with pre-recorded messages using Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP). Some even call it SPIT which stands for "Spam over Internet Telephony". Email, Internet applications and other Voice over IP systems are vulnerable to abuse by attackers who instigate unsolicited and unwanted communications.
Telemarketers, prank callers, and other telephone system abusers are increasingly targeting VoIP. The technology behind this threat is SIP (Session Initiation Protocol, IETF ¨C Internet Engineering Task Force, RFC 3261) which has has been supported by major telecommunication vendors, and could become the industry standard for voice, video and other types of interactive communication including instant messaging and gaming.
References
Useful Links & Recommended Threads - Wilders Security Forums
www.techsupportalert.com/
www.freedrweb.com/cureit/?lng=en
www.malwarebytes.org/mbam.php
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/.../bb897445.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/.../bb896653.aspx
www.glaryutilities.com/
http://miekiemoes.blogspot.com/2008/...gain-sigh.html
Emsisoft Knolwedgebase: What is a computer worm? Find and remove worms with Emsisoft Anti-Malware.
http://www.virusbtn.com/conference/v...astMinute7.xml
PC Security - Lunarsoft Wiki
http://forum.avast.com/index.php?topic=55588.0
http://www.spywareterminator.com/sup...s-spyware.aspx
RKill - What it does and What it Doesn't - A brief introduction to the program <-Thanks for Rkill
Last edited:
